Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dessler HRM12e PPT 01
Uploaded by
Mohamed salahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dessler HRM12e PPT 01
Uploaded by
Mohamed salahCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1
Introduction to
Human Resource
Management
Part One | Introduction
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook
publishing as Prentice Hall The University of West Alabama
WHERE WE ARE NOW
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 12
LEARNING OUTCOMES
1. Explain what human resource management is and how
it relates to the management process.
2. Show with examples why human resource management
is important to all managers.
3. Illustrate the human resources responsibilities of line
and staff (HR) managers.
4. Briefly discuss and illustrate each of the important
trends influencing human resource management.
5. List and briefly describe important trends in human
resource management.
6. Define and give an example of evidence-based human
resource management.
7. Outline the plan of this book.
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 13
Human Resource Management at Work
What Is Human Resource Management (HRM)?
The process of acquiring, training, appraising, and compensating
employees, and of attending to their labor relations, health and
safety, and fairness concerns.
Organization
People with formally assigned roles who work together to
achieve the organizations goals.
Manager
The person responsible for accomplishing the organizations
goals, and who does so by managing the efforts of the
organizations people.
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 14
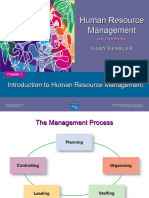
The Management Process
Planning
Controlling Organizing
Leading Staffing
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 15
Human Resource Management Processes
Acquisition
Fairness Training
Human
Resource
Management
Health and Safety (HRM) Appraisal
Labor Relations Compensation
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 16
Personnel Aspects of a Managers Job
Conducting job analyses
Planning labor needs and recruiting job candidates
Selecting job candidates
Orienting and training new employees
Managing wages and salaries
Providing incentives and benefits
Appraising performance
Communicating
Training and developing managers
Building employee commitment
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 17
Personnel Mistakes
Hire the wrong person for the job
Experience high turnover
Have your people not doing their best
Waste time with useless interviews
Have some employees think their salaries are unfair and
inequitable relative to others in the organization
Allow a lack of training to undermine your departments
effectiveness
Commit any unfair labor practices
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 18
Basic HR Concepts
The bottom line of managing:
Getting results
HR creates value by engaging in activities
that produce the employee behaviors that
the organization needs to achieve its
strategic goals.
Looking ahead: Using evidence-based
HRM to measure the value of HR activities
in achieving those goals.
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 19
Line and Staff Aspects of HRM
Line Manager
Is authorized (has line authority) to direct the work of
subordinates and is responsible for accomplishing the
organizations tasks.
Staff Manager
Assists and advises line managers.
Has functional authority to coordinate personnel activities
and enforce organization policies.
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 110
Line Managers HRM Responsibilities
1. Placing the right person on the right job
2. Starting new employees in the organization (orientation)
3. Training employees for jobs that are new to them
4. Improving the job performance of each person
5. Gaining creative cooperation and developing smooth
working relationships
6. Interpreting the firms policies and procedures
7. Controlling labor costs
8. Developing the abilities of each person
9. Creating and maintaining department goals
10. Protecting employees health and physical condition
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 111
Human Resource Specialties
Recruiter
Labor relations
specialist EEO coordinator
Human
Resource
Specialties
Training specialist Job analyst
Compensation
manager
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 114
High-Performance Work Systems
Increase productivity and performance by:
Recruiting, screening and hiring more effectively
Providing more and better training
Paying higher wages
Providing a safer work environment
Linking pay to performance
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 121
KEY TERMS
organization
manager
management process
human resource management (HRM)
authority
line authority
staff authority
line manager
staff manager
functional authority
globalization
human capital
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall 124
You might also like
- Dessler HRM12e PPT 01Document36 pagesDessler HRM12e PPT 01Nway Moe SaungNo ratings yet
- Human ResourcesDocument32 pagesHuman ResourcesAli WsxNo ratings yet
- Dessler - HRM - First SessionDocument15 pagesDessler - HRM - First SessionharryjohnlyallNo ratings yet
- CH.1 Introduction. Strategic HRMDocument40 pagesCH.1 Introduction. Strategic HRMnadya shafirah100% (1)
- Dessler HRM12e PPT 01Document28 pagesDessler HRM12e PPT 01Muhammad MuaviaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource Management: Global Edition 12eDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Management: Global Edition 12eMuhammadAxadKhataabGujjarNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management at WorkDocument18 pagesHuman Resource Management at WorkTamanna AkterNo ratings yet
- Module-1 HRMDocument21 pagesModule-1 HRMJijo MathewNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource Management: Global Edition 12eDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Management: Global Edition 12eumerNo ratings yet
- Dessler HRM12e PPT 01Document30 pagesDessler HRM12e PPT 01harryjohnlyallNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource Management: Global Edition 12eDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Management: Global Edition 12eRabin DhunganaNo ratings yet
- 1st Chapter Slides of HRM Garry Dessler AmendedDocument43 pages1st Chapter Slides of HRM Garry Dessler AmendedMaarijNo ratings yet
- HRM 2020Document246 pagesHRM 2020K59 Nguy?n L� Qu� Tr�nNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HRM (Chap 1B)Document33 pagesIntroduction To HRM (Chap 1B)MUHAMMEDNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (HRM)Document42 pagesChapter 1 (HRM)Naila GujjarNo ratings yet
- CHP 1Document20 pagesCHP 1Nahan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction HRMDocument30 pagesChapter One Introduction HRMmustafekhadiir6No ratings yet
- Lect 1 IntroDocument18 pagesLect 1 IntroMohamed NakeebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document12 pagesLecture 3Sarfaraz Siddique 173No ratings yet
- Human Resources Management - 2023Document21 pagesHuman Resources Management - 2023n71736745No ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementSAAD SIDDIQUINo ratings yet
- HRM Claas June 4, 2016Document35 pagesHRM Claas June 4, 2016Agha Muhammad MujahidNo ratings yet
- Bangor Transfer Abroad ProgrammeDocument23 pagesBangor Transfer Abroad ProgrammeSivaraman P. S.No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument42 pagesHuman Resource ManagementAkhil Ranjan TarafderNo ratings yet
- Lecture#1 - Introduction To HRMDocument8 pagesLecture#1 - Introduction To HRMAbdul WaheedNo ratings yet
- The Strategic Role of HRM2Document13 pagesThe Strategic Role of HRM2edraul_rodlac2No ratings yet
- Ch1 - Introducton To HRMDocument49 pagesCh1 - Introducton To HRMmojoo2003No ratings yet
- Chap 1.introduction To HRMDocument26 pagesChap 1.introduction To HRMTip SceneNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 11eDocument31 pagesHuman Resource Management 11egame rangersNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementnatlyhNo ratings yet
- Ch1 HRDocument25 pagesCh1 HRAparna TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ch1 HRDocument25 pagesCh1 HRAnonymous bwz9Rq6xtjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 HRMDocument31 pagesChapter 1 HRMABDULLAH MUHAMMAD RAFIQ ANWARNo ratings yet
- Ch1 HRDocument25 pagesCh1 HRActor CharumaNo ratings yet
- HRM Chapter 1 ShafiDocument26 pagesHRM Chapter 1 ShafiHelik SoniNo ratings yet
- Dessler - hrm15 - Inppt - 01Document42 pagesDessler - hrm15 - Inppt - 01Kaiye KaiyeNo ratings yet
- Dessler - hrm15 - Inppt - 01 OFDocument28 pagesDessler - hrm15 - Inppt - 01 OFMd. Masudur Rahman MasumNo ratings yet
- CH 1 HRM GarryDocument32 pagesCH 1 HRM GarryMurugesanNo ratings yet
- Desser Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument28 pagesDesser Chapter 1 IntroductionKhaled AbozeedNo ratings yet
- HRM - Muhammad Bilal KhanDocument12 pagesHRM - Muhammad Bilal Khanomermirza2009No ratings yet
- Week 1 Introduction To HRMDocument26 pagesWeek 1 Introduction To HRMSs ArNo ratings yet
- HRM101 Ch1Document41 pagesHRM101 Ch1Basheer Al-GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Dessler - hrm15 - Inppt - 01Document33 pagesDessler - hrm15 - Inppt - 01Amany Sayed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document39 pagesChapter 1uzairNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementTaz UddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To HRM CoordinatedDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To HRM CoordinatedPUNK ASSNo ratings yet
- Suply Chain ManagementDocument34 pagesSuply Chain ManagementUday KovuriNo ratings yet
- Dessler - hrm14 - PPT - 01Document34 pagesDessler - hrm14 - PPT - 01Prio DebnathNo ratings yet
- ELP Intro To Human ResourceDocument217 pagesELP Intro To Human Resourcejothi subraNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 12e - 7Document46 pagesHuman Resource Management 12e - 7Monica RizkaNo ratings yet
- Dessler Hrm15 Inppt 01Document42 pagesDessler Hrm15 Inppt 01Mohammed SafiNo ratings yet
- Dessler-Chapter 1Document13 pagesDessler-Chapter 1Fatih BIYIKLINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - HRM IntroductionDocument46 pagesChapter 1 - HRM IntroductionAzhar HassanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementHadi345214No ratings yet
- Training and Developing Employees: Global Edition 12eDocument47 pagesTraining and Developing Employees: Global Edition 12eRohit Kumar 4170No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document30 pagesChapter 1NNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HRMDocument30 pagesIntroduction To HRMalkaNo ratings yet
- The Simple Side Of Human Resource ManagementFrom EverandThe Simple Side Of Human Resource ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Strategy-Driven Talent Management: A Leadership ImperativeFrom EverandStrategy-Driven Talent Management: A Leadership ImperativeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Coaching To Enhance Performance®: How Successful Leaders Create Sustainability DifferentlyFrom EverandCoaching To Enhance Performance®: How Successful Leaders Create Sustainability DifferentlyNo ratings yet
- HRD Part 1: Hello@Edutap - Co.In 1Document49 pagesHRD Part 1: Hello@Edutap - Co.In 1Preetam Sharma100% (1)
- Ethics in The WorkplaceDocument3 pagesEthics in The WorkplaceMani DebanterNo ratings yet
- LITERATURE REVIEW of JRGDocument3 pagesLITERATURE REVIEW of JRGsalmaNo ratings yet
- SmartQuestionnaire HarrisonAssessmentsDocument2 pagesSmartQuestionnaire HarrisonAssessmentsHavid ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - Motivation Among Workers in Large and Diversified Business OrganizationsDocument9 pagesHuman Resource Management - Motivation Among Workers in Large and Diversified Business OrganizationsRohan PorelNo ratings yet
- How To Reduce Employee TurnoverDocument6 pagesHow To Reduce Employee TurnoverKiraNo ratings yet
- Bakker 2008Document45 pagesBakker 2008Pascia SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- 2012 Rolle Bahamian Public ServiceDocument14 pages2012 Rolle Bahamian Public ServiceMaimouna NdiayeNo ratings yet
- Leadership TeslaDocument6 pagesLeadership TeslaKendice ChanNo ratings yet
- Assessment 4. Ramirez Ria Jane JDocument4 pagesAssessment 4. Ramirez Ria Jane JRiajane RamirezNo ratings yet
- MBA ABM SyllabusDocument33 pagesMBA ABM Syllabuszinga007No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Job SatisfactionDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 1: Job SatisfactionAzrul AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Impact of Performance Appraisal Systems On Employee ProductivityDocument11 pagesImpact of Performance Appraisal Systems On Employee ProductivityOvidius OhwovorioleNo ratings yet
- The Role of Personal Characteristics To Develo1Document5 pagesThe Role of Personal Characteristics To Develo1Putri Delan RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Performance Management 2023-2Document53 pagesPerformance Management 2023-2iharuna640No ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 - Job - Analysis - and - Work - Design - 9eDocument17 pagesChapter - 4 - Job - Analysis - and - Work - Design - 9ePriyanjaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Motivation Concepts and Their ApplicationsDocument44 pagesChapter Four Motivation Concepts and Their Applicationsamrudin eliasNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument5 pagesResearch PaperTooba SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Razan Rihani - CVDocument2 pagesRazan Rihani - CVRazan RihaniNo ratings yet
- Essential Elements For Recruitment and Retention - Generation YDocument20 pagesEssential Elements For Recruitment and Retention - Generation YSu ZentNo ratings yet
- Abhijit Chakraborti: Profile SummaryDocument4 pagesAbhijit Chakraborti: Profile SummaryHRD CORP CONSULTANCYNo ratings yet
- Syllabus OB 24Document5 pagesSyllabus OB 24huylong0702No ratings yet
- B.A. Hons PsychologyDocument42 pagesB.A. Hons PsychologySankalpa Nagamuwa100% (1)
- Human Resource عبانم يرش بDocument27 pagesHuman Resource عبانم يرش بNaseebullah PasoonNo ratings yet
- HRM NotesDocument73 pagesHRM NotesKashvi JindalNo ratings yet
- Project Leadership in Health Care HEAL8140: Week 12Document19 pagesProject Leadership in Health Care HEAL8140: Week 12AnnaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Brief 2Document4 pagesAssignment Brief 2Hương ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Appriasal Letter Format-OriginalDocument1 pageAppriasal Letter Format-Originalvenustaffing100% (1)
- Journal of Economic Psychology: Bård Kuvaas, Robert Buch, Antoinette Weibel, Anders Dysvik, Christina G.L. NerstadDocument15 pagesJournal of Economic Psychology: Bård Kuvaas, Robert Buch, Antoinette Weibel, Anders Dysvik, Christina G.L. NerstadScopusLockNo ratings yet
- Current Issues in Organisational BehaviourDocument11 pagesCurrent Issues in Organisational Behavioursilhoutteangel100% (2)