Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 11
Uploaded by
Subash Barsingh Thapa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views16 pagesleadership styles
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentleadership styles
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views16 pagesChapter 11
Uploaded by
Subash Barsingh Thapaleadership styles
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Leadership
• leading from the front
•Making followers leaders
•Influencing the behaviors of others towards the goal
achievement
•It is all about inspiring the people
•Getting things done or making things happen
•According to
•Stephen P Robbins- Leadership is the ability to
influence a group toward the achievement of goals
•Stoner, Freeman and Gilbert- Leadership is the
process of directing and influencing the task related
activities of group members
Leadership Styles
Autocratic styles, Democratic, Free Rein Styles
◦ Autocratic
Power and decision-making are centralized in the
leader
Has three major features- dictator, centralization,
limiting the participation of follower
Believe in rewards and punishments
Information is controlled by the leader
◦ Democratic
Based on theory ‘Y’ model of Mc Gregor
Based on the Mc Gregor’s theory ‘X’ concept
Power and decision making is decentralized
Followers are motivated to co-operated to with leader
◦ Subordinates consults, discuss and participate in
decision making
◦ Enough authority is given to the followers
◦ Performance based rewards and punishment
Free-Rein(Laissez-Faire Style)
◦ power and decision making is entrusted in the
followers
◦ Gives freedom to make decision and complete work
◦ Serves as information provider and has low authority
◦ Subordinates set their own goals
◦ Effective for research and creative job areas
Managerial Grid Style of Leadership
It is a nine-by-nine matrix outlining 81 different leadership styles,
more emphasis in five styles
Has two behavioral dimensions “Concern for People” and
“Concern for Production ”
◦ 1.1 Improvised Style
◦ little concern for both people and production
◦ 9.1 Task Manager
High concern for production and low concern for people
◦ 1.9 Country Club Style
High concern for people and low concern for production
◦ 9.9 Team Builder Style
Concern for both people and production
◦ 5.5 Middle-of-the-Roader Style
Balanced concern for people and production
Situational Leadership Styles
Focused on two orientation i.e Tasks and Relationship
orientation
Leader defines roles for followers and the task done by them
in the task orientation and likewise the leader has close
personal relationship with the followers and open
communication as well
leaders are born according to situation as specific style is
appropriate for all situations
according to this there are four- leadership styles
High task- low relationship- more focus on task or job
High relationship-low task- focus on the feelings of employees
High task-high relationship- focus on both relationship & tasks
Low task-low relationship- little focus on both relationship
and tasks
Four system of Leadership
System1: Exploitative-Authoritative
◦ Autocratic leaders
◦ Excessive use of power & high desire for control over others
◦ Has no confidence and trust in subordinates
◦ No freedom to followers
System 2: Benevolent Authoritative
◦ Has some confidence and trust in subordinates
◦ Less freedom to work
◦ Leader sometimes gets ideas and opinion of followers
System 3: Participative
◦ Substantial but not complete confidence and trust on
followers
◦ Subordinates feels free to discuss things about job
◦ Leader usually gets ideas and opinion of subordinates
System 4: Consultative
◦ Leader has complete confidence and trust on
followers
◦ Followers fells completely free to discuss job
related things
◦ Appreciate follower’s ideas and opinions
Leadership Theories
Trait approach to leadership
◦ Considered personal qualities and characteristics
differentiate leaders from non-leaders
◦ focuses on identifying different personality traits and
characteristics that are linked to successful leadership across
a variety of situations
◦ There are so many traits that leaders might posses
among them major six traits are associated with
leadership
Achievement drive: High level of effort, high levels of
ambition, energy and initiative
Leadership motivation: an intense desire to lead others
to reach shared goals
Honesty and integrity: trustworthy, reliable, and open
Self-confidence: Belief in one’s self, ideas, and ability
Cognitive ability: Capable of exercising good judgment,
strong analytical abilities, and conceptually skilled
Knowledge of business: Knowledge of industry and
other technical matters
Emotional Maturity: well adjusted, does not suffer from
severe psychological disorders.
Others: charisma, creativity and flexibilit
Behavioral Theory
a leader behavior as the best predictor of his leadership
influences and as a result, is the best determinant of his or
her leadership success
According to this theory leader can be made through
teaching them the most appropriate behavioral response
for any given situation
Two types of Behavioral Theory
Ohio State University (1940s)
the primary purposes of the study was to identify common
leadership behaviors. After compiling and analyzing the
results, the two types of behavior were identified
Initiating Structure (Task Oriented Leaders)
◦ leader focuses their behaviors on the organizational
structure, the operating procedures and they like to keep
control
Consideration (People Oriented behavioral Leader
◦ The people oriented leaders are focuses the inner needs
of the people
◦ seek to motivate their staff through the human relation,
Encouraging, Observing, Listening, Coaching and Mentoring
etc
The Michigan Studies
Done by researchers at Michigan University
Purpose of this research was to determine
the pattern of leadership behaviors that
results in effective group performance
Job-centered leader behavior
◦ Pay close attention to the work of subordinates
◦ Main focus is on efficiency and task performance
Employee-centered leader behavior
◦ Focus on human aspects of the group
◦ Concern is to build effective work groups
Situational Approach
Effectiveness of leaders depends upon the
situations
There is no one best way o be leader or to
exercise leadership
If situation changes, leader needs to change
his or her style
For example: when unskilled, untrained and
uneducated employees autocratic style
might work but if the employees are well-
trained, educated and skilled participative or
free style will appropriate
Fiedler’s Contingency Model
◦ Group performance depends upon the leader’s style and
situation around him
◦ Classifies leadership styles into
Task oriented- focus on task only
Relations oriented- concern relationship with
subordinates
◦ Also identified three important situational factors
Leader-member relations- whether or not the
subordinates like or trust leader
Task structure- extent to which group’s tasks, goals,
performances are clearly defined
Position power- extent to which leader uses controls,
rewards, and punish subordinates
Path-Goal Theory
Developed by Robert House
Leaders can enhance motivation by linking
rewards with performance
Leaders have to clarify the subordinates the
goals they have to achieve and path they
have to follow to reach that goals
Motivation is done through
◦ Clarifying goals
◦ Linkage between goals and rewards
◦ Directing path to goals
Leader Behaviors Environmental
Subordinates’ Personal Characteristics
Characteristics •Directive
•Supportive •Task Structure
•Perceived ability •Authority system
•Locus of control •Participative
•Achievement Oriented •Work group
Subordinates’ motivation to perform
You might also like
- Chapter Four: Recruitment, Selection and SocializationDocument49 pagesChapter Four: Recruitment, Selection and SocializationSubash Barsingh ThapaNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument12 pagesLeadershipSubash Barsingh ThapaNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument14 pagesPlanningSubash Barsingh ThapaNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument14 pagesPlanningSubash Barsingh ThapaNo ratings yet
- CL Chap3Document28 pagesCL Chap3Subash Barsingh ThapaNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Comparision ICSE CBSEDocument3 pagesComparision ICSE CBSErkumarrkNo ratings yet
- Proactive Inclusive Learning PlanDocument7 pagesProactive Inclusive Learning PlanAna CastroNo ratings yet
- Blooms Taxonomy PresentationDocument31 pagesBlooms Taxonomy PresentationThirumalaimuthukumaranMohanNo ratings yet
- O'Byrne Philosophy StatementDocument22 pagesO'Byrne Philosophy StatementIan O'ByrneNo ratings yet
- LC 8b Oral Comm Lesson PlanDocument13 pagesLC 8b Oral Comm Lesson PlanKarla Andrea AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- Washback of An English Achievement Test On Teachers' Perceptions at A Vietnamese UniversityDocument18 pagesWashback of An English Achievement Test On Teachers' Perceptions at A Vietnamese UniversityĐỗ Quỳnh TrangNo ratings yet
- HANDSOUT Chapter 4 Curriculum Designing and Organization (Group 2)Document3 pagesHANDSOUT Chapter 4 Curriculum Designing and Organization (Group 2)Maezelle Anne AliviaNo ratings yet
- CO OP AOTA - July - 2020Document10 pagesCO OP AOTA - July - 2020Ana Claudia GomesNo ratings yet
- POS Supervisory ProgramDocument3 pagesPOS Supervisory ProgramForchia CutarNo ratings yet
- Job-Embedded Learning Output: Names of Scholar/s: PST Section: ProgramDocument2 pagesJob-Embedded Learning Output: Names of Scholar/s: PST Section: ProgramCARLOS FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
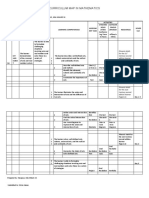
- Curriculum Map in Mathematics: Phoenix Math For The 21 Century Second Edition Learner Page2-24Document2 pagesCurriculum Map in Mathematics: Phoenix Math For The 21 Century Second Edition Learner Page2-24Ogaban JamilNo ratings yet
- Lets Review4Document4 pagesLets Review4Sunshine BorerNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Positive AttitudeDocument2 pagesThe Benefits of Positive AttitudePriyaSbmNo ratings yet
- Exam Multiple Choice TemplateDocument2 pagesExam Multiple Choice TemplateFlorencio CoquillaNo ratings yet
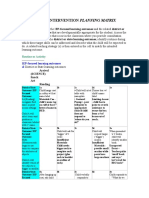
- Sample Intervention Planning MatrixDocument2 pagesSample Intervention Planning MatrixOyeesugarNo ratings yet
- Flatland: An: Integrated Math & Language Arts UnitDocument12 pagesFlatland: An: Integrated Math & Language Arts UnitThom JohnsonNo ratings yet
- DLL Lesson Plan in Arts q1 WK 5Document6 pagesDLL Lesson Plan in Arts q1 WK 5Mitzi Faye CabbabNo ratings yet
- 1stQ Week1Document12 pages1stQ Week1Sinamar Blas LaroyaNo ratings yet
- World of Self, Family and Friends UNIT 4 - Lunchtime Speaking 40 Wednesday Friendship LanguageDocument16 pagesWorld of Self, Family and Friends UNIT 4 - Lunchtime Speaking 40 Wednesday Friendship LanguageAin NawwarNo ratings yet
- Grading SystemDocument20 pagesGrading SystemFil IlaganNo ratings yet
- Bascaran, Solano, Nueva Vizcaya: S9ES - Ia-J36.6Document4 pagesBascaran, Solano, Nueva Vizcaya: S9ES - Ia-J36.6Arceli Valdoz DomingoNo ratings yet
- Portfolio EditingDocument17 pagesPortfolio EditingKristine ToralbaNo ratings yet
- Action Plan in REading ProgramDocument3 pagesAction Plan in REading ProgramLyrehs L.M.100% (2)
- Pearson - Aimsweb Assessment Instrument Description - CODocument10 pagesPearson - Aimsweb Assessment Instrument Description - CORodger HortonNo ratings yet
- Part 2. Planning A Lesson or A Series of Lessons PDFDocument7 pagesPart 2. Planning A Lesson or A Series of Lessons PDFMaksym BuchekNo ratings yet
- Weekly Output Monitoring Tool of TeachersDocument9 pagesWeekly Output Monitoring Tool of TeachersAteiluj Oretnip NitubalNo ratings yet
- Nabulao NHS LAC Plan MAPAREDocument4 pagesNabulao NHS LAC Plan MAPAREMonica P. RamosNo ratings yet
- Teacher and Student Perceptions of The Methods Used in Teaching and Learning English Secondary Writing SkillsDocument2 pagesTeacher and Student Perceptions of The Methods Used in Teaching and Learning English Secondary Writing SkillsMiftahul HusnaNo ratings yet
- Learning Styles by Dunn and DunnDocument4 pagesLearning Styles by Dunn and DunnMei-Mei ÜNo ratings yet
- Content Performance 2 Syllabus 2ND SemDocument2 pagesContent Performance 2 Syllabus 2ND Semarold bodoNo ratings yet