Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Write Once, Run Anywhere Nishad Abdulkareem, Lecturer MES College Marampally
Uploaded by
Anonymous 9IZzd0MhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Write Once, Run Anywhere Nishad Abdulkareem, Lecturer MES College Marampally
Uploaded by
Anonymous 9IZzd0MhCopyright:
Available Formats
write once, run anywhere
Nishad Abdulkareem, Lecturer
MES College Marampally
• Java Programming language
• History
• Java Varieties
• Java world
• Buzz words
• Classpath
• Program
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
Java Programming Language
• Java is a programming language originally developed by
James Gosling at Sun Microsystems (which is now a
subsidiary of Oracle Corporation) and released in 1995 as a
core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform.
• The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but
has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities.
• Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode (class
file) that can run on any Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
regardless of computer architecture.
• It is intended to let application developers "write once, run
anywhere".
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
Once upon a time…
• The original and reference implementation Java compilers,
virtual machines, and class libraries were developed by Sun
from 1995.
• As of May 2007, in compliance with the specifications of the
Java Community Process, Sun relicensed most of its Java
technologies under the GNU General Public License.
•
• James Gosling initiated the Java language project in June 1991
for use in one of his many set-top box projects.
• Java was originally designed for interactive television, but it
was too advanced.[ The language, initially called Oak after an
oak tree that stood outside Gosling's office, also went by the
name Green and ended up later renamed as Java, from a list of
random words.
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
…and grown up like…
• Sun Microsystems released the first public implementation as
Java 1.0 in 1995. It promised "Write Once, Run Anywhere"
(WORA), providing no-cost run-times on popular platforms.
• Fairly secure and featuring configurable security, it allowed
network- and file-access restrictions. Major web browsers
soon incorporated the ability to run Java applets within web
pages, and Java quickly became popular.
• With the advent of Java 2 (released initially as J2SE 1.2 in
December 1998–1999), new versions had multiple
configurations built for different types of platforms.
• The different platforms are J2EE,J2ME and J2SE
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
Behind the names…
• Java Platform, Enterprise Edition or Java EE is a widely
used platform for server programming in the Java
programming language.
• The Java platform (Enterprise Edition) differs from the Java
Standard Edition Platform (Java SE) in that it adds libraries
which provide functionality to deploy fault-tolerant,
distributed, multi-tier Java software, based largely on modular
components running on an application server.
• For marketing purposes, Sun renamed new J2 versions as
Java EE. The current version is called Java EE 6.
• Java EE includes several API specifications, such as JDBC,
RMI, e-mail, JMS, web services, XML, etc, and defines how
to coordinate them.
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
JSE
• Java Standard Edition or Java SE is a widely used platform
for programming in the Java language.
• It is the Java Platform used to deploy portable applications for
general use.
• In practical terms, Java SE consists of a virtual machine,
which must be used to run Java programs, together with a set
of libraries (or "packages") needed to allow the use of file
systems, networks, graphical interfaces, and so on, from
within those programs.
• The "SE" is used to distinguish the base platform from Java
EE and Java ME. The "2" was originally intended to
emphasize the major changes introduced in version 1.2, but
was removed in version 1.6.
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
JME
• Java Platform, Micro Edition, or Java ME, is a Java
platform designed for mobile devices and embedded systems.
• Target devices range from industrial controls to mobile phones
(especially feature phones) and set-top boxes. Java ME was
formerly known as Java 2 Platform, Micro Edition (J2ME).
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
JEE
• Java EE also features some specifications unique to Java EE
for components. These include Enterprise JavaBeans,
Connectors, servlets, portlets (following the Java Portlet
specification), JavaServer Pages and several web service
technologies.
• This allows developers to create enterprise applications that
are portable and scalable, and that integrate with legacy
technologies.
• A Java EE application server can handle transactions, security,
scalability, concurrency and management of the components
that are deployed to it, in order to enable developers to
concentrate more on the business logic of the components
rather than on infrastructure and integration tasks
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
Java World
Provides a simplified, fast way to
create dynamic web content. JSP
technology enables rapid
Java Server Pages development of web-based
applications that are server- and
platform-independent.
Java Servlets
A servlet class
Messaging extends
is a method the capabilities
of communication
Java Messaging Services of servers
between that host
software applications
components or that are
accessed bya way
applications. of a request-response
messaging client can send
programming
messages to and receive messages servlets
model. Although from any
Web applications can use the Java mail API can respond
other to any
client. Each type
client of request,
connects to a they
JavaMail API to send email are commonly
messaging agentused to extend
that provides the for
facilities
notifications. The API has applications
creating, hosted
sending, by web
receiving, andservers
reading
two parts: an application- messages.Eg Car inventory
level interface that the
application components use Java API for XML Processing
to send email and a service
provider interface. Service
providers implement The Java API for XML
particular email protocols, Processing (JAXP), part of the
such as SMTP JDBC API Java SE platform, supports the
processing of XML documents
using the Document Object
Model (DOM), the Simple API
for XML (SAX),
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
JRE
• Java Runtime Environment
The java programming language adds the portability by
converting the source code to byte code version which can
be interpreted by the JRE and gets converted to the
platform specific executable ones.
Thus for different platforms one has corresponding
implementation of JRE. But JRE has to meet the
specification JVM (Java Virtual Machine) Concept that
serves as a link between the Java libraries and the platform
specific implementation of JRE.
Thus JVM helps in the abstraction of inner
implementation from the programmers who make use of
libraries for their programmes.
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
• Science Behind Java
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
JDK
Java Developer Kit contains tools needed to develop the Java
programs, and JRE to run the programs. The tools include
compiler (javac.exe), Java application launcher (java.exe),
Appletviewer, etc…
The JDK(Java Developmental Tool kit) comes along with java
libraries and JVM embedded in it.
Apart from these it comes along with the utility tools for byte
code compilation "javac", Executing the byte codes through java
programmes through "java" and many more utilities found in the
binary directory of java.
Speaking practically JDK is essential for developers, which
comes along with library packages to develop Software
programmes.
JRE is minimal set of programmes which executes the java class
files developed by the software developers.
Without jre one can only compile the application but cannot run
the application Since jre contains the JVM which executes the
byte code generated from the javac compiler.
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
• JRE = JVM + Java Packages Classes(like util, math, lang,
awt,swing etc)+runtime libraries.
• Java Runtime Environment contains JVM, class libraries, and
other supporting files. It does not contain any development
tools such as compiler, debugger, etc. Actually JVM runs the
program, and it uses the class libraries, and other supporting
files provided in JRE. If you want to run any java program,
you need to have JRE installed in the system
• The Java Virtual Machine provides a platform-independent
way of executing code; programmers can concentrate on
writing software, without having to be concerned with how or
where it will run
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
• As we all aware when we compile a Java file, output is not an 'exe'
but it's a '.class' file. '.class' file consists of Java byte codes which are
understandable by JVM. Java Virtual Machine interprets the byte
code into the machine code depending upon the underlying operating
system and hardware combination. It is responsible for all the things
like garbage collection, array bounds checking, etc… JVM is
platform dependent.
• The JVM is called "virtual" because it provides a machine interface
that does not depend on the underlying operating system and machine
hardware architecture. This independence from hardware and
operating system is a cornerstone of the write-once run-anywhere
value of Java programs.
• There are different JVM implementations are there. These may differ
in things like performance, reliability, speed, etc. These
implementations will differ in those areas where Java specification
doesn’t mention how to implement the features, like how the garbage
collection process works is JVM dependent, Java spec doesn’t define
any specific way to do this.
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
• JVM
• ByteCode
• JIT
• Applets
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
Java Buzzwords
• Simple
Java inherits the C/C++ syntax and many of the object
oriented features of C++ ,most programmers have little
trouble learning java.
• Object Oriented
The object model in java is Simple and easy to extend,
while primitive types ,such as integers ,are kept as high
performance nonobjects.
• Robust
Memory management
Exception Handling
• Multithreaded
Multiprocess synchronization
• Architectural Neutral
• Distributed
RMI
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
Classpath
• The Classpath is an argument - set either on the command-
line, or through an environment variable - that tells the Java
Virtual Machine where to look for user-defined classes and
packages when running Java programs.
• When we invoke Java, we specify the name of the application
to run: org.mypackage.HelloWorld. However we must
also tell Java where to look for the files and directories
defining our package. So to launch the program, we use the
following command:
java -classpath D:\myprogram
org.mypackage.HelloWorld
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
Say hello to Java
• First Program
All program starts by executing by calling main()
Public is the access specifier.main must be declared as
public so that it can access from outside the class
static allows main to be called without instantiating a
particular class.
Any information that are passed in to the method is
received by variables specified within the parenthesis
called parameters .
String args[] declares a parameter named args,
which is an array of instances of string.
System is predefined class that provides access to
system, out is the output stream that is connected to the
console
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
• Any information need to pass to a method is specified
within the set of parameters that follow the name of
method_called parameters
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
• Swap two numbers without using a third variable
• Reverse Number
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
javap - The Java Class File Disassembler
• The javap command disassembles a class file. Its output
depends on the options used. If no options are used, javap
prints out the package, protected, and public fields and
methods of the classes passed to it. javap prints its output to
stdout. For example, compile the following class declaration:
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
• help Prints out help message for javap.
-l Prints out line and local variable tables.
-b Ensures backward compatibility with javap in
JDK 1.1.
-public Shows only public classes and members.
-protected Shows only protected and public
classes and members.
-package Shows only package, protected, and
public classes and members. This is the default.
-private Shows all classes and members.
-Jflag Pass flag directly to the runtime system.
Some examples: javap -J-version javap -J-
Djava.security.manager -J-
Djava.security.policy=MyPolicy MyClassName
-s Prints internal type signatures.
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
• -c Prints out disassembled code, i.e., the instructions that
comprise the Java bytecodes, for each of the methods in the
class. These are documented in the Java Virtual Machine
Specification.
• -verbose Prints stack size, number of locals and args for
methods.
• -classpath path Specifies the path javap uses to look
up classes. Overrides the default or the CLASSPATH
environment variable if it is set. Directories are separated by
semi-colons. Thus the general format for path is:
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
References
• www.wikipedia.com
• http://www.sun.com
• http://www.java-examples.com/
• The complete Reference Java
Department of MCA MES College Marampally
You might also like
- New To Java?: Basics of Java TechnologyDocument5 pagesNew To Java?: Basics of Java Technologymalli.gontla3724No ratings yet
- EJ Unit 1Document48 pagesEJ Unit 1o kNo ratings yet
- Advance Java OverviewDocument5 pagesAdvance Java OverviewPapu BhoiNo ratings yet
- 3 - Unit I - Chapter I - Understanding Java EEDocument15 pages3 - Unit I - Chapter I - Understanding Java EEVishal ChaurasiyaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Scope: 3.1.1 Login ModuleDocument59 pages1.1 Scope: 3.1.1 Login ModuleShivang SethiyaNo ratings yet
- Java 1Document99 pagesJava 1kaviarasu100% (1)
- Basic Java EE BookDocument211 pagesBasic Java EE BookKondalarao SuravarapuNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument36 pagesIntroductionREESHU RANJANNo ratings yet
- 1.history of Java 2. Evolution of Java, 3.datatypes, Variables and Arrays. 4.operators. 5.control StatementsDocument47 pages1.history of Java 2. Evolution of Java, 3.datatypes, Variables and Arrays. 4.operators. 5.control StatementsAbrar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Java Beans (EJB) : T.Y.I.T Sem-V Enterprise JavaDocument25 pagesEnterprise Java Beans (EJB) : T.Y.I.T Sem-V Enterprise Javaarchana palNo ratings yet
- J2ee WebtehDocument237 pagesJ2ee Webtehrip975No ratings yet
- Building and Deploying Reliable High-Performance Java ApplicationsDocument4 pagesBuilding and Deploying Reliable High-Performance Java ApplicationsatilabayatNo ratings yet
- Open BookDocument20 pagesOpen BookMG GalactusNo ratings yet
- Core Java Notes: Chapter-1, 2,3 Features of JAVA EnvironmentDocument31 pagesCore Java Notes: Chapter-1, 2,3 Features of JAVA EnvironmentRUSHIL SHAHNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 JavaDocument8 pagesUnit 1 Javapraveen.jagtap191No ratings yet
- Seth White Alexandre Alves David RorkeDocument8 pagesSeth White Alexandre Alves David RorkecarmenmpNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Websphere Application Server - Part 2: Ibm and Business Partner Sales Training OnlyDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Websphere Application Server - Part 2: Ibm and Business Partner Sales Training OnlyNoureddine OussouNo ratings yet
- TD Bos Javafx ChoDocument92 pagesTD Bos Javafx Choapi-3717772100% (3)
- Sun Java™ Composite Application Platform Suite: Complete, Secure, Scalable SOA-Based IntegrationDocument5 pagesSun Java™ Composite Application Platform Suite: Complete, Secure, Scalable SOA-Based IntegrationSundar N PasupathyNo ratings yet
- Basics of Java Programming LanguageDocument32 pagesBasics of Java Programming LanguageDr Narayana Swamy RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Software EnvironmentDocument24 pagesSoftware Environmentmahesh gurramNo ratings yet
- Suspicious EmailDocument44 pagesSuspicious EmailishitaNo ratings yet
- Integrating Java and Matlab Components Into The Same Parallel and Distributed Application Using JavaportsDocument10 pagesIntegrating Java and Matlab Components Into The Same Parallel and Distributed Application Using Javaportsjayaram_scaj3921No ratings yet
- Features of JavaDocument4 pagesFeatures of JavaNixie Lee MarintesNo ratings yet
- Electricity Bill Management System: Software Description A. JavaDocument7 pagesElectricity Bill Management System: Software Description A. JavaShivansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Java Everywhere A Comprehensive GuideDocument8 pagesJava Everywhere A Comprehensive Guidemhesenli7No ratings yet
- Enterprise ApplicationDocument47 pagesEnterprise ApplicationAlka SinghNo ratings yet
- Ejava Unit 01Document15 pagesEjava Unit 01noNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Web Publishing With Java Why Java?Document20 pagesUnit Iii Web Publishing With Java Why Java?srikmarepallyNo ratings yet
- Bca 6044 Research PaperDocument7 pagesBca 6044 Research PaperShivansh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Learn JavaDocument8 pagesLearn JavaSean Kibs AlexNo ratings yet
- Trails Covering The BasicsDocument2 pagesTrails Covering The BasicsPaulo BuñayNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Introduction To Java ElementsDocument30 pagesChapter-2 Introduction To Java ElementsKorsa KorsaNo ratings yet
- J2EE Software EnvironmentDocument20 pagesJ2EE Software EnvironmentsureshNo ratings yet
- Java Technology: Portable Object Oriented RobustDocument6 pagesJava Technology: Portable Object Oriented RobustYogendra BaisNo ratings yet
- Nisarg Mehta: Senior Java Developer Contact # 815 719 9889Document5 pagesNisarg Mehta: Senior Java Developer Contact # 815 719 9889Heerain Parikh VitthalbhaiNo ratings yet
- Building Java HTTP ServletsDocument35 pagesBuilding Java HTTP ServletsKumar SudhirNo ratings yet
- Recruitment Support SystemDocument55 pagesRecruitment Support SystemIdeonix SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Why JavaDocument21 pagesWhy JavakarthickamsecNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction JavaDocument14 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction JavaTuyền Nhữ VănNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction JavaDocument14 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction JavaTuyền Nhữ VănNo ratings yet
- Maxine: An Approachable Virtual Machine For, and In, Java: Ments, Debuggers, Memory Management, Compilers, OptimizationDocument24 pagesMaxine: An Approachable Virtual Machine For, and In, Java: Ments, Debuggers, Memory Management, Compilers, OptimizationAndreas AndronikakisNo ratings yet
- 2Sr. Java Developer Resume Example Company Name - Jersey City, New JerseyDocument7 pages2Sr. Java Developer Resume Example Company Name - Jersey City, New JerseyksraowNo ratings yet
- Advanced Java (Module 2)Document36 pagesAdvanced Java (Module 2)Sushma SumantNo ratings yet
- Java Security White PaperDocument9 pagesJava Security White PaperGabriel ParedesNo ratings yet
- Introducing The Ibm Websphere Application Server Version 4.0 For Z/Os and Os/390Document15 pagesIntroducing The Ibm Websphere Application Server Version 4.0 For Z/Os and Os/390Mohammed Saad EddinNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Advance JavaDocument5 pagesSyllabus Advance JavaOwais PatelNo ratings yet
- Component Technology Notes 4 PDFDocument22 pagesComponent Technology Notes 4 PDFharsh vardhanNo ratings yet
- EJ Unit 4Document39 pagesEJ Unit 4Yexo KajNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument336 pagesJavaPradeep Venu TNo ratings yet
- Universidad Politécnica de Aguascalientes Ingeniería en Sistemas Estratégicos de InformaciónDocument5 pagesUniversidad Politécnica de Aguascalientes Ingeniería en Sistemas Estratégicos de InformaciónChristian MicheleNo ratings yet
- Parallel Computing Using Java Mobile AgentsDocument8 pagesParallel Computing Using Java Mobile AgentsSek AustinNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Database Management SystemDocument33 pages1.1 Introduction To Database Management SystemvasaviNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Use Java?: Glossary Web Publishing With JavaDocument21 pagesWhy Do We Use Java?: Glossary Web Publishing With JavaS Kalyan LakshmanNo ratings yet
- CMP 325 Javatech NoteDocument92 pagesCMP 325 Javatech Noterexdum7No ratings yet
- 1 - Java BasicsDocument42 pages1 - Java Basicskareem mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Various Java Web FrameworksDocument3 pagesPerformance Analysis of Various Java Web FrameworksShivkant DohaliyaNo ratings yet
- JAVA: Java Programming for beginners teaching you basic to advanced JAVA programming skills!From EverandJAVA: Java Programming for beginners teaching you basic to advanced JAVA programming skills!No ratings yet
- Getting Inside Java - Beginners Guide: Programming with Java by Prem KumarFrom EverandGetting Inside Java - Beginners Guide: Programming with Java by Prem KumarNo ratings yet
- DB2 Tech Talk PureData Systems Presentation PDFDocument65 pagesDB2 Tech Talk PureData Systems Presentation PDFkaishidenNo ratings yet
- DC Choppers: Prof. T.K. Anantha Kumar, E&E Dept., MSRITDocument103 pagesDC Choppers: Prof. T.K. Anantha Kumar, E&E Dept., MSRITSaranya. M SNSNo ratings yet
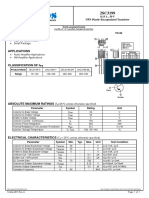
- C3199 DatasheetDocument1 pageC3199 Datasheetalexmihai_scribdNo ratings yet
- ONYXSWORKDocument4 pagesONYXSWORKMuhammad Azizi SubariNo ratings yet
- Timer and Counter Instructions: Dr. Manjula Sutagundar Dept. of E&IE, BEC, BagalkotDocument114 pagesTimer and Counter Instructions: Dr. Manjula Sutagundar Dept. of E&IE, BEC, BagalkotManjula SutagundarNo ratings yet
- Low Power Autonomous Controller Fcn-Rtu: Network-Based Control SystemDocument4 pagesLow Power Autonomous Controller Fcn-Rtu: Network-Based Control SystemosmondmanurungNo ratings yet
- LogcatDocument197 pagesLogcatAdheShenzaNo ratings yet
- Zeta ConverterDocument42 pagesZeta ConverterJabez E JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Why Use PROFIBUS For Process AutomationDocument4 pagesWhy Use PROFIBUS For Process AutomationAshish RawatNo ratings yet
- Dell Networking 6.1.0.6 Release NotesDocument107 pagesDell Networking 6.1.0.6 Release NotesasdfNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v3.1 Module 2 Networking FundamentalsDocument57 pagesCCNA 1 v3.1 Module 2 Networking FundamentalsPŘincê ÂĻĩNo ratings yet
- Roles in Database EnvironmentDocument25 pagesRoles in Database EnvironmentJustin Rodriguez67% (15)
- PC AssemblyDocument14 pagesPC Assemblyyuan salayogNo ratings yet
- Atari ST Basic To CDocument250 pagesAtari ST Basic To CremowNo ratings yet
- MJL21193 21194Document6 pagesMJL21193 21194DiosmeHenrnadezNo ratings yet
- Solution Architecture Document SAD TemplateDocument16 pagesSolution Architecture Document SAD Templatesikandar jameel100% (3)
- Prog GuideDocument250 pagesProg GuideculebrasxxxNo ratings yet
- Enterasys Wireless ® Convergence Software User Guide Version 8.11Document208 pagesEnterasys Wireless ® Convergence Software User Guide Version 8.11Sergio AcunaNo ratings yet
- Lenovo 3000 H Series ManualDocument29 pagesLenovo 3000 H Series ManualSofia Gomez LopezNo ratings yet
- XBT Xa800eDocument108 pagesXBT Xa800eAlberto Suazo BasaezNo ratings yet
- BDC Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesBDC Questions and AnswerssatishNo ratings yet
- CompTIA® A+ Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) Cert Guide PDFDocument1,162 pagesCompTIA® A+ Core 1 (220-1101) and Core 2 (220-1102) Cert Guide PDFApril Oxox94% (16)
- SDIO SDmode ControllerDocument4 pagesSDIO SDmode ControllerDinh Hoang TungNo ratings yet
- 725B Configuration Software Rev 2Document110 pages725B Configuration Software Rev 2Mohamed SobhyNo ratings yet
- MUCARBT200 ManualDocument31 pagesMUCARBT200 ManualNawi LaraNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Datastage 7.5X2 and Datastage 8.0.1 VersionsDocument2 pagesDifference Between Datastage 7.5X2 and Datastage 8.0.1 Versionsprasanth_irsNo ratings yet
- Unit4 WorkbookDocument1 pageUnit4 WorkbookLaura Duran OzoriaNo ratings yet
- Copiadora Acard Technology ARS-2033Document88 pagesCopiadora Acard Technology ARS-2033Alfredo De San SalvadorNo ratings yet
- How Amplifiers Work1 by NafeesDocument5 pagesHow Amplifiers Work1 by NafeesnafeesNo ratings yet
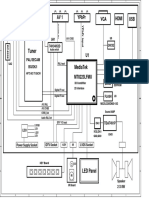
- Schematic MTK8223L PDFDocument9 pagesSchematic MTK8223L PDFdreamyson198360% (5)