Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project Proposal
Uploaded by
Akash Srivastav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views11 pagesA proposal is a request for financial assistance to implement a project. The proposal outlines the plan of the implementing organisation about the project, giving extensive information about the intention, for implementing it, the ways to manage it and the results to be delivered from it .The following guidelines are designed to help you prepare your full proposal. How well you plan the action is critical to the success of the project.
Original Title
Project Proposal PPT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA proposal is a request for financial assistance to implement a project. The proposal outlines the plan of the implementing organisation about the project, giving extensive information about the intention, for implementing it, the ways to manage it and the results to be delivered from it .The following guidelines are designed to help you prepare your full proposal. How well you plan the action is critical to the success of the project.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views11 pagesProject Proposal
Uploaded by
Akash SrivastavA proposal is a request for financial assistance to implement a project. The proposal outlines the plan of the implementing organisation about the project, giving extensive information about the intention, for implementing it, the ways to manage it and the results to be delivered from it .The following guidelines are designed to help you prepare your full proposal. How well you plan the action is critical to the success of the project.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Project Proposal Writing
Dr. Yogesh Chandra Srivastava,
D.Phil,
Subject Matter Specialist (Agricultural Extension),
Directorate of Extension,
Sam Higginbottom University of Agriculture,
Technology and Sciences,
Allahabad, U.P., India
Executive Summary
• A proposal is a request for financial assistance
to implement a project. The proposal outlines
the plan of the implementing organisation
about the project, giving extensive information
about the intention, for implementing it, the
ways to manage it and the results to be
delivered from it .The following guidelines are
designed to help you prepare your full
proposal. How well you plan the action is
critical to the success of the project.
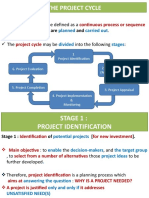
Introduction
• A project proposal is a detailed description of a series of activities
aimed at solving a certain problem. In order to be successful, the
document should:
• Provide a logical presentation of a research idea
• Illustrate the significance of the idea
• Show the idea's relationship to past actions
• Articulate the activities for the proposed project
• Designing a project is a process consisting of two elements, which
are equally important and thus essential to forming a solid project
proposal:
• Project planning (formulation of project elements)
• Proposal writing (converting the plan into a project document)
• The project proposal should be a detailed and directed
manifestation of the project design. It is a means of presenting the
project to the outside world in a format that is immediately
recognised and accepted.
Getting Ready to Start a Project Proposal
• From vision to proposal:
• The first step is to decide what the problem is and develop a rough
idea (vision) of how this could be solved. This vision is then to be
transformed into an idea for a specific project proposal.
• A logical framework may help you to structure this idea in a
systematic way, and clearly define the aim, purpose, outputs,
activities, means, costs and the methodologies for monitoring and
evaluation, and will thus from the basis for the preparation of the
narrative of the proposal.
• Remember that your idea may have to fit certain requirements if
you are answering to a call for proposals, and that it must also fit
local policies and frameworks.
• Identify potential funding options: It is necessary to find out in
advance what sources of funding are available, through
governments, international cooperation agencies, some
international NGOs or private foundations.
Getting Ready to Start a Project Proposal
Build a project proposal team:
• A leader will be needed to manage the proposal development in an efficient way,
and therefore it is advisable to assign the lead role to one specific person.
• This person is then responsible for the coordination of the overall proposal
development, for communication with potential funders and for making sure that
all different pieces of input are brought together in a consistent and coherent text.
• Experts with more detailed technical knowledge might be part of the team, or
simply contribute to an initial brainstorming session.
• Furthermore, the budget should be compiled in close cooperation with staff from
the financial department.
• Input from stakeholders or other specialists with different backgrounds helps bring
in the necessary expertise to the project.
Hold a kick-off meeting:
• It is helpful to discuss and develop the proposal in a small team and share drafts
with experts of all relevant disciplines not just from within the administration, but
also from outside it.
• Input from stakeholders or other specialists with different backgrounds helps bring
in the necessary expertise, but also a larger variety of ideas on how to solve a
particular issue and achieve the previously agreed objectives.
Proposal Writing
Proposal Writing
• The requirements of content and format of
proposals differ noticeably from one
sponsoring agency to another. While some
may provide their own application forms to be
filled, and others may request on-line
submission of proposals, others will accept a
proposal in any format as long as it features
the necessary information, and does not
contradict their conditions
Proposed Format for a Full Project Proposal
Title page:
• A title page should appear on proposals longer than three to four pages. The title
page should indicate the project title, the name of the lead organisation (and
potential partners, if any), the place and date of project preparation and the name
of the donor agency to whom the proposal is addressed.
Project title:
• The project title should be short, concise, and preferably refer to a certain key
project result or the leading project activity. Project titles that are too long or too
general fail to give the reader an effective snapshot of what is inside.
Abstract/Executive Summary:
• Many readers lack the time needed to read the whole project proposal. It is
therefore useful to insert a short project summary, an abstract or executive
summary. The abstract should include: the problem statement, the project’s
objectives, implementing organisations; key project activities; and potentially the
total project budget. Theoretically, the abstract should be compiled after the
relevant items already exist in their long form. For a small project the abstract may
not be longer than 10 lines. Bigger projects often provide abstracts as long as two
pages.
Context:
• This part of the project describes the social, economic, political and cultural
background from which the project is initiated. It should contain relevant data
from research carried out in the project planning phase or collected from other
sources.
Proposed Format for a Full Project Proposal
Target group:
• Define the target group and show how it will benefit from the project.
• The project should provide a detailed description of the size and
characteristics of the target groups, and especially of direct project
beneficiaries.
Project implementation:
• The implementation plan should describe activities and resource
allocation in as much detail as possible.
• It is exceptionally important to provide a good overview of who is going to
implement the project’s activities, as well as when and where.
• The implementation plan may be divided into two key elements: the
activity plan and the resource plan.
• The activity plan should include specific information and explanations of
each of the planned project activities.
• The duration of the project should be clearly stated, with considerable
detail on the beginning and the end of the project.
Proposed Format for a Full Project Proposal
Budget:
• An itemised summary of an organisation’s expected income and expenses
over a specified period of time.
Monitoring and evaluation:
• The basis for monitoring is set when the indicators for results are set. The
project proposal should indicate: how and when the project management
team will conduct activities to monitor the project’s progress; which
methods will be used to monitor and evaluate; and who will do the
evaluation.
Reporting:
• The schedule of project progress and financial report could be set in the
project proposal. Often these obligations are determined by the standard
requirements of the donor agency. The project report may be compiled in
different versions, with regard to the audience they are targeting.
Management :
• A brief description should be given of the project personnel, the individual
roles each one has assumed, and the communication mechanisms that
exist between them. All the additional information (such as CVs) should be
attached to the annexes.
Thanks
You might also like
- Grant Proposal TemplateDocument3 pagesGrant Proposal TemplateMark Dwayne Cyrus IINo ratings yet
- Purpose of Small Grants and GuidelinesDocument6 pagesPurpose of Small Grants and GuidelinesClement AZENDANo ratings yet
- Fund Raising BasicsDocument23 pagesFund Raising Basicsdennis8113No ratings yet
- 1.customer Service Representative CV TemplateDocument2 pages1.customer Service Representative CV TemplatePrabath Danansuriya100% (1)
- Lecture 5 Designing HRD ProgramsDocument26 pagesLecture 5 Designing HRD ProgramsVeerendranath NaniNo ratings yet
- Proposal Writing TipsDocument2 pagesProposal Writing TipsganeshisNo ratings yet
- Potter & Perry Ch1Document17 pagesPotter & Perry Ch1Francis ObmergaNo ratings yet
- Conceptpaper PDFDocument1 pageConceptpaper PDFJay Luke UmoruNo ratings yet
- Proposal Writing ManualDocument49 pagesProposal Writing Manualpayankey100% (1)
- Community Capacity Building Program: Proposal WritingDocument33 pagesCommunity Capacity Building Program: Proposal WritingkeerthadinnuNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument8 pagesProject ProposalTariq Rajput100% (1)
- Project Proposal FormatDocument3 pagesProject Proposal FormatPrecious Jan AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines To Monitoring and Evaluation - CARE UgandaDocument153 pagesGuidelines To Monitoring and Evaluation - CARE UgandaDejan ŠešlijaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Rural Banking and Micro Financing 1Document16 pagesChapter 4 Rural Banking and Micro Financing 1saloniNo ratings yet
- Proposal ComponentsDocument3 pagesProposal ComponentsAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Program Evaluation: A Brief Introduction ..Document13 pagesProgram Evaluation: A Brief Introduction ..Micheal SamsonNo ratings yet
- Gender Audit QuestionnaireDocument5 pagesGender Audit Questionnairerio angelika100% (3)
- Donor Funded Project RequirementDocument8 pagesDonor Funded Project RequirementBUKENYA BEEE-2026100% (1)
- Portage Lake Watershed Support Grant ApplicationDocument9 pagesPortage Lake Watershed Support Grant ApplicationArielle BreenNo ratings yet
- Writing A Research ProposalDocument2 pagesWriting A Research ProposalIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Guide Consultant Fees Jan 2Document19 pagesGuide Consultant Fees Jan 2Langa Kambi-ShambaNo ratings yet
- Porposal WritingDocument102 pagesPorposal WritingMoustapha AlexNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument16 pagesProject ProposalJasper de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Employment Vacancy - PDT Country Director AfghanistanDocument4 pagesEmployment Vacancy - PDT Country Director AfghanistanBill JeffreyNo ratings yet
- M&E Training ManualDocument45 pagesM&E Training Manualsheittie100% (1)
- Guidelines For Writing A Project ProposalDocument11 pagesGuidelines For Writing A Project ProposalJehadAbuSalim100% (1)
- How To Write A Good CV 1Document4 pagesHow To Write A Good CV 1jeronimo marconniNo ratings yet
- Project AppraisalDocument15 pagesProject AppraisalTesfanesh Ethiopia100% (1)
- CD Burundi-Rwanda FinalDocument5 pagesCD Burundi-Rwanda FinaliihaoutreachNo ratings yet
- Tution ProposalDocument9 pagesTution ProposalUsman AliNo ratings yet
- 21.1.6 Gender AuditDocument50 pages21.1.6 Gender AuditHARLEEN KAUR100% (1)
- Assignment On Organizational CultureDocument13 pagesAssignment On Organizational Culturemonicca869581No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document45 pagesChapter 4Ermi Ye Emaya LigNo ratings yet
- Handouts Project ProposalDocument30 pagesHandouts Project Proposalsurendra100% (4)
- Information Processing McLaughlin Et Al PDFDocument24 pagesInformation Processing McLaughlin Et Al PDFRobert HutchinsonNo ratings yet
- Lead - Auditor - (IRCA) - ISO - 9001 - 2015 - Yogyakarta PDFDocument2 pagesLead - Auditor - (IRCA) - ISO - 9001 - 2015 - Yogyakarta PDFagus witonoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Service Quality On Customer Loyalty: A Study of Hotels in EthiopiaDocument10 pagesEffect of Service Quality On Customer Loyalty: A Study of Hotels in EthiopiaIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- 10 Writing Project ProposalsDocument52 pages10 Writing Project ProposalsMakewa100% (6)
- How Strategic Is HRMDocument16 pagesHow Strategic Is HRMShalinee SewbundhunNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and ControllingDocument5 pagesMonitoring and ControllingMohit MalikNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument10 pagesProposalregineNo ratings yet
- Project DesignDocument46 pagesProject DesignDemalyn DemandanteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - FINAL CurriculumDocument79 pagesChapter 3 - FINAL CurriculumMitch ComiaNo ratings yet
- Critical ThinkingDocument33 pagesCritical Thinkingtondutosuau0% (1)
- PMD Pro Project ManagementDocument51 pagesPMD Pro Project Managementben100% (1)
- ROLE OF Information TECHNOLOGY IN SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT-2Document37 pagesROLE OF Information TECHNOLOGY IN SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT-2ved254910198% (120)
- How To Write A Successful Project Proposal - NGO Resource Centre - AfghanistanDocument8 pagesHow To Write A Successful Project Proposal - NGO Resource Centre - AfghanistanAsadullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Adama Training ManualDocument43 pagesAdama Training ManualWoldeab DanielNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Livelihood Analysis: (Frank Ellis)Document12 pagesA Framework For Livelihood Analysis: (Frank Ellis)didarNo ratings yet
- The Logical Framework: "Logframe": Verifiable Indicators and The ContractDocument34 pagesThe Logical Framework: "Logframe": Verifiable Indicators and The ContractJess Zausa MasulaNo ratings yet
- Curriclum Revised 1st DraftDocument73 pagesCurriclum Revised 1st Draftamaruthivaraprasad100% (1)
- CH 7 Social Groups and OrganizationsDocument25 pagesCH 7 Social Groups and OrganizationsKhaela Mercader100% (1)
- AEB 422 Lecture Notes April 02 - 09 - 2021 Project Cycle - IdentificationDocument6 pagesAEB 422 Lecture Notes April 02 - 09 - 2021 Project Cycle - IdentificationThabo ChuchuNo ratings yet
- Project IdentificationDocument89 pagesProject Identificationtadgash4920100% (3)
- Research ProposalDocument16 pagesResearch ProposalGundeepNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Review of Related LiteratureDocument35 pages3.2 Review of Related LiteratureSoleil MaxwellNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX 1 AC Budget Narrative Sample Template 2016Document5 pagesAPPENDIX 1 AC Budget Narrative Sample Template 2016ASQIRIBANo ratings yet
- Interorganizational CommunicationDocument32 pagesInterorganizational CommunicationRara AlonzoNo ratings yet
- BestConstructionPracticesBUDMWorkshop Midwest FlyerDocument2 pagesBestConstructionPracticesBUDMWorkshop Midwest FlyerKevin ParkerNo ratings yet
- Adinan Sufiyan, Individual Assignment of Mini-Research Community and Development PsychologyDocument37 pagesAdinan Sufiyan, Individual Assignment of Mini-Research Community and Development PsychologyDukkana BariisaaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Project?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Project?Max MbiseNo ratings yet
- CV NMTC ApplicationDocument8 pagesCV NMTC ApplicationStephen GallutiaNo ratings yet
- LEAP Programme Project Reporting GuidelinesDocument8 pagesLEAP Programme Project Reporting Guidelinesapi-36963390% (1)
- Title Thesis ProposalDocument3 pagesTitle Thesis ProposalLaurence Rue AudineNo ratings yet
- The Process of Community DevelopmentDocument20 pagesThe Process of Community DevelopmentGiven Msomba100% (1)
- Training and Development of Library StaffDocument27 pagesTraining and Development of Library StaffAM100% (1)
- Project Life CycleDocument2 pagesProject Life Cyclefathermother5No ratings yet
- Week 3 - Project ProposalDocument28 pagesWeek 3 - Project ProposalEskinderNo ratings yet
- HDS 4107 LECTURE SESSION SEVEN ModDocument7 pagesHDS 4107 LECTURE SESSION SEVEN ModAggieNo ratings yet
- Agro - Industries Prospects and ChallengesDocument33 pagesAgro - Industries Prospects and ChallengesAkash SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Presented To: Dr. Prashant Mario D'Souza Er. Ashish Kumar Kerketta Presented By: Shivam Kumar 13BTAG118Document17 pagesPresented To: Dr. Prashant Mario D'Souza Er. Ashish Kumar Kerketta Presented By: Shivam Kumar 13BTAG118Akash SrivastavNo ratings yet
- 32 Project ManagementDocument252 pages32 Project ManagementAjay MalikNo ratings yet
- Thinking About Purposes, Audiences, and Technologies: How Is "Writing" Defined?Document9 pagesThinking About Purposes, Audiences, and Technologies: How Is "Writing" Defined?Tyler FinleyNo ratings yet
- Project Plan Odessa Mobile Technology ProjectDocument22 pagesProject Plan Odessa Mobile Technology Projectsan1432No ratings yet
- Issues Essay Template - ModifiedDocument19 pagesIssues Essay Template - ModifiedmathhoangNo ratings yet
- DLC Ilm Course GuideDocument18 pagesDLC Ilm Course GuideAlexandruNo ratings yet
- Vmware Solution Strategy and Roadmap Services Solution OverviewDocument2 pagesVmware Solution Strategy and Roadmap Services Solution OverviewВиктор АтанасовNo ratings yet
- Bma Specialty Doctor Specialist and Consultant Roles and Responsibilities Comparison Table Jul 2021Document1 pageBma Specialty Doctor Specialist and Consultant Roles and Responsibilities Comparison Table Jul 2021Shahab AnsariNo ratings yet
- United States v. Athanasios Theodoropoulos, A/K/A "Tommy". Appeal of Athanasios Theodoropoulos. United States of America v. George Karivalis, A/K/A "Papou". Appeal of George Karivalis. United States of America v. Jimmy Peetros, United States of America v. John Bourzikos, United States of America v. Constantinos Tsokas, A/K/A "Gus". Appeal of Constantinos Tsokas. United States of America v. Nestor Barrera, United States of America v. Dimitrios Argiris, A/K/A "Angelo". Appeal of Dimitrios Argiris. United States of America v. Haralambos Trelopoulos, A/K/A "Charlie". Appeal of Haralambos Trelopoulos, 866 F.2d 587, 3rd Cir. (1989)Document19 pagesUnited States v. Athanasios Theodoropoulos, A/K/A "Tommy". Appeal of Athanasios Theodoropoulos. United States of America v. George Karivalis, A/K/A "Papou". Appeal of George Karivalis. United States of America v. Jimmy Peetros, United States of America v. John Bourzikos, United States of America v. Constantinos Tsokas, A/K/A "Gus". Appeal of Constantinos Tsokas. United States of America v. Nestor Barrera, United States of America v. Dimitrios Argiris, A/K/A "Angelo". Appeal of Dimitrios Argiris. United States of America v. Haralambos Trelopoulos, A/K/A "Charlie". Appeal of Haralambos Trelopoulos, 866 F.2d 587, 3rd Cir. (1989)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Collaborative ModelDocument38 pagesCollaborative ModelakhilNo ratings yet
- Unleash The Full Power of Your Palo Alto Networks TechnologyDocument19 pagesUnleash The Full Power of Your Palo Alto Networks TechnologyharshadraiNo ratings yet
- IR Global - 2022 Membership PackDocument40 pagesIR Global - 2022 Membership Packwneo1982No ratings yet
- International Master of Science in Fire Safety Engineering: InhoudDocument3 pagesInternational Master of Science in Fire Safety Engineering: InhoudDaniel Montilla NavasNo ratings yet
- Listening Without Ears Artificial IntelligenceDocument16 pagesListening Without Ears Artificial IntelligenceColin LewisNo ratings yet
- AGS - CSD - Hazmat AdvisorDocument38 pagesAGS - CSD - Hazmat AdvisorK DesmetNo ratings yet
- Teaching Writing... Ends and MeansDocument18 pagesTeaching Writing... Ends and MeansIbrahim HossainNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Framework and Exam RoadmapsDocument6 pagesConsolidated Framework and Exam Roadmapsabdullah hamidNo ratings yet
- How Case-Based Methods Can Automate Fluidic Circuit DesignDocument12 pagesHow Case-Based Methods Can Automate Fluidic Circuit DesignCarlos GomezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Teacher As A PersonDocument21 pagesChapter 1 The Teacher As A PersonJhomar EncisoNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For Civil EngineersDocument3 pagesCode of Ethics For Civil EngineersGustavo Ameri Lopez CadilloNo ratings yet
- Alan P Rossiter's 8 Aspects of Proffessional ExcellenceDocument9 pagesAlan P Rossiter's 8 Aspects of Proffessional Excellencechahna mehta100% (1)
- Expert System On Inventory ManagementDocument43 pagesExpert System On Inventory ManagementBello MadaNo ratings yet
- 21 Skills You Must Test For A Perfect Call Center - AssessmentDocument16 pages21 Skills You Must Test For A Perfect Call Center - AssessmentmrmdnadimNo ratings yet