Professional Documents
Culture Documents
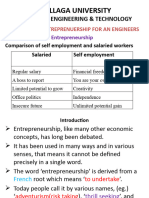
Definition of Entrepreneurship: Chapter One-Entrepreneurship and Free Enterprise
Uploaded by
ZELALEM SAMUEL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views22 pagesentrepreneurship
Original Title
Chapter 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documententrepreneurship
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views22 pagesDefinition of Entrepreneurship: Chapter One-Entrepreneurship and Free Enterprise
Uploaded by
ZELALEM SAMUELentrepreneurship
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Chapter one-Entrepreneurship and Free Enterprise
1.1. Definition of Entrepreneurship
entrepreneurship is the process and entrepreneur is
the person undertaking entrepreneurial activity.
Entrepreneurship can be defined from different
prospective as follows:
• Entrepreneurship is the process of creating incremental
wealth.
• The wealth is created by those individuals who assume
the major risk in terms of equity and time or providing
value for others.
• Entrepreneurship can also be defined as the process of
creating something different and better with value by
devoting the necessary time and effort by assuming the,
accompanying financial, psychic and social risks and
receiving the resulting monetary reward and personal
satisfaction.
• In this case an individual should come up with something
different and better in order to be named as entrepreneur.
The third definition views the term from four
perspectives; i.e. from the economist, psychologist,
business man and capitalist philosophers’ point of view.
To an economist an entrepreneur is one who brings
resource, labor, materials, and other assets into
combination that makes their value greater than before
and also one who introduces changes & innovations.
To a psychologist an entrepreneur is a person typically driven by
certain forces need to obtain or attain something, to experiment,
to accomplish or perhaps to escape the authority of others.
For a business man entrepreneur is either a threat (aggressive
competitor) or an ally (source of supply, consumer, etc).
For the capitalist philosopher an entrepreneur is one who creates
wealth for others as well, who finds better way to utilize
resources and reduce waste and who produce job others are glad
to get.
In general, the process of entrepreneurship includes five
critical elements. They are:
• The ability to perceive an opportunity.
• The ability to commercialize the perceived opportunity i.e.
innovation
• The ability to pursue it on a sustainable basis.
• The ability to pursue it through systematic means.
• The acceptance of risk or failure
Based on the above concepts of entrepreneurship, an
entrepreneur can be defined as follows:
An entrepreneur is someone who perceives an opportunity
and creates an organization to pursue it with the intention of
being profitable.
Entrepreneurship – Historical Perspective
• Here let us took in to the historical development of
entrepreneurship so as to grasp the meaning of the word
entrepreneurship.
• During the ancient period the word entrepreneur was used
to refer to a person managing large commercial projects
through the resources provided to him.
In the 17th Century a person who has signed a
contractual agreement with the government to
provide stipulated products or to perform service
was considered as entrepreneur.
In this case the contract price is fixed so any
resulting profit or loss reflects the effort of the
entrepreneur.
• In the 18th Century the first theory of entrepreneur
has been developed by Richard Cantillon.
• He said that an entrepreneur is a risk taker. If we
consider the merchant, farmers and /or the
professionals they all operate at risk.
• For example, the merchants buy products at a
known price and sell it at unknown price and this
shows that they are operating at risk.
• The other development during the 18th Century is the
differentiation of the entrepreneurial role from capital
providing role.
• The later role is the base for today’s venture capitalist.
• In the late 19th and early 20th Century an entrepreneur was
viewed from economic perspectives. The entrepreneur
organizes and operates an enterprise for personal gain.
• In the middle of the 20th Century the notion of an
entrepreneur as an inventor has established.
• Apply untried technological possibility for producing
new commodities or producing an old one in a new
way or opening a new outlet for products by
reorganizing a new industry.”
• The concept of innovation and newness are at the heart of
the above definition.
• Entrepreneurship involves innovation and untried
technologies or what we called creative destruction, which
is defined as the process whereby existing product process,
ideas, and business are replaced with better ones
• Through the process of creative destruction,
old and outdated approaches and products
are replaced with better ones.
1.3The Role of Entrepreneur within the
Economy
1. Promotes Capital Formation
2. Creates Large-Scale Employment Opportunities
3. Promotes Balanced Regional Development
4. Reduces Concentration of Economic Power
5. Wealth Creation and Distribution
6. Increasing Gross National Product and Per Capita
Income
7. Improvement in the Standard of Living
8. Promotes Country's Export Trade
9. Induces Backward and Forward Linkages
10. Facilitates Overall Development
1.4. Entrepreneurship – Creativity and Innovation
• Discussions about innovation are often made difficult
because people are unclear about the exact meanings of
some key terms.
• In particular there is confusion about the difference between
creativity and innovation. Let us start with some definitions:
• Creativity is the capability or act of conceive something
original or unusual.
• Creativity emphasizes the “ability” not the “activity” of
bringing something new in to existence.
• Creativity occurs when an individual visualizes new
patterns in his/ her mind.
• Creativity is a fuzzy idea and cannot be clarified until it is
mad in to prototype, where we can touch it, test it and show
it to others.
• At this point, the creation becomes an invention as the stage
where a creative idea has been reduced in to practice.
• Invention is the creation of something that has never
been made before and is recognized as the product of
some unique insight.
• Innovation is the implementation of something new.
• If you have a brainstorm meeting and dream up
dozens of new ideas then you have displayed
creativity but there is no innovation until something
gets implemented.
• Somebody has to take a risk and deliver something for a
creative idea to be turned into an innovation.
• Innovation is different from invention.
• An invention is discovery of new methods and new
materials, where as innovation is utilization of inventions to
produce new and better quality of products that give greater
satisfaction to the consumer and higher profits to the
entrepreneur..
• An inventor gives the idea and an innovator implements the
idea for economic gain.
• Some individuals can be both inventor and innovator
• The innovator (entrepreneur) commercially exploits the
invention produced by him or by any other person.
• Innovation is the process of doing new things. Ideas have
little value until they are converted in to new products,
services, or processes.
• There are many people who conceive new ideas but do not
take action to implement them.
• Innovation, therefore, is the transformation of creative ideas
in to useful applications, but creativity is a prerequisite to
innovation.
• If creativity is the seed that inspires entrepreneurship,
innovation is the process of entrepreneurship.
• Therefore innovation is the process of taking a creative idea
and turned it in to product or process that can be used or
sold.
Cont’d
Results in new
The creation of Knowledge
Invention
something new
Innovation The transformation of an Results in new products,
idea or resources into Services, or processes
useful application
You might also like
- The Self-Made Billionaire Effect (Review and Analysis of Sviokla and Cohen's Book)From EverandThe Self-Made Billionaire Effect (Review and Analysis of Sviokla and Cohen's Book)No ratings yet
- Food Cost ControlDocument7 pagesFood Cost ControlAtul Mishra100% (1)
- Deposition Hugh Burnaby Atkins PDFDocument81 pagesDeposition Hugh Burnaby Atkins PDFHarry AnnNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 Introdution To EntreprenuershipDocument34 pagesChapter - 1 Introdution To EntreprenuershipmohammedkasoNo ratings yet
- The Digital Future FinanceDocument17 pagesThe Digital Future FinanceMid VillepinteNo ratings yet
- Theories of Development and Indian Economy PDFDocument119 pagesTheories of Development and Indian Economy PDFSudhanshu Bele100% (3)
- Chapter One: The Concepts of Entrepreneurship and EntrepreneurDocument17 pagesChapter One: The Concepts of Entrepreneurship and Entrepreneurras dawitNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Nature of Enterpreneurship Up DatedDocument42 pagesCh-1 Nature of Enterpreneurship Up Dateddini best100% (1)
- Synopsis Movie Ticket BookingDocument18 pagesSynopsis Movie Ticket BookingRaj Bangalore17% (6)
- Wellington Investment v. TrajanoDocument1 pageWellington Investment v. TrajanoNicole Kalingking100% (1)
- CondrenDocument303 pagesCondrenbebelizaNo ratings yet
- Cassino To The Alps - US Army Center of Military HistoryDocument625 pagesCassino To The Alps - US Army Center of Military HistoryBootlead BootleadingNo ratings yet
- Creativity and InnovationDocument16 pagesCreativity and InnovationAdil LoveNo ratings yet
- Executing Innovation: Expert Solutions to Everyday ChallengesFrom EverandExecuting Innovation: Expert Solutions to Everyday ChallengesNo ratings yet
- Iso 27001Document84 pagesIso 27001sboukhal100% (2)
- Darab Rules of Procedure - SUMMARY ON FEW SECTIONSDocument2 pagesDarab Rules of Procedure - SUMMARY ON FEW SECTIONSNilsy Ynzon100% (2)
- Innovation-Principles and SourcesDocument6 pagesInnovation-Principles and Sourcessuriya kishoreNo ratings yet
- CH - 1Document35 pagesCH - 1jebinamokonen2No ratings yet
- Ent. Presentation 1Document53 pagesEnt. Presentation 1bekelewudu6No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship & Business Dev'tDocument35 pagesEntrepreneurship & Business Dev'tTariku MehdiNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship.: U.C Develop Understanding of Entrepreneurship (DUE)Document31 pagesEntrepreneurship.: U.C Develop Understanding of Entrepreneurship (DUE)FifakeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Nature of EntrepreneurshipDocument21 pagesChapter 1: The Nature of Entrepreneurshipetetu weldeNo ratings yet
- Introdution To EntreprenuershipDocument27 pagesIntrodution To EntreprenuershipOld Oromo music museumNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument30 pagesChapter Oneyomif tamiruNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship For Engineers: (Ceng5211)Document42 pagesEntrepreneurship For Engineers: (Ceng5211)Gemechis BekeleNo ratings yet
- CreatAndInnovate - PPT 20230908 135539 0000Document16 pagesCreatAndInnovate - PPT 20230908 135539 0000RajkumarNo ratings yet
- IM 642 - Introduction and OverviewDocument18 pagesIM 642 - Introduction and OverviewMassoudNo ratings yet
- Enterprenurship FInalDocument148 pagesEnterprenurship FInalrajamritdas3No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship ILIDocument135 pagesEntrepreneurship ILIDany TadNo ratings yet
- CH 1 (Autosaved)Document44 pagesCH 1 (Autosaved)Wêēdhzæmē ApdyræhmæåñNo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Zakeria Eid Ismail MSC of EconomicsDocument44 pagesLecturer: Zakeria Eid Ismail MSC of EconomicsWêēdhzæmē ApdyræhmæåñNo ratings yet
- Samara University College of Business and Economics: Department of Management EntrepreneurshipDocument54 pagesSamara University College of Business and Economics: Department of Management Entrepreneurshipfentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship MaterialDocument85 pagesEntrepreneurship Materialashu tkNo ratings yet
- Concept of EntrepreneurshipDocument33 pagesConcept of EntrepreneurshipAnkush ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Chap 1 NoteDocument22 pagesEntrepreneurship Chap 1 NoteNahom DiresNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - EdDocument126 pagesUnit-1 - EdRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Unit 1Document46 pagesEntrepreneurship Unit 1khushboosharma2010No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Chapter One WetmDocument24 pagesEntrepreneurship Chapter One Wetmgeorge manNo ratings yet
- ED Important Questions With AnswerDocument12 pagesED Important Questions With AnswernagarajanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Developing Entrepreneurial Creativity and Innovation 33Document33 pagesTopic 3 - Developing Entrepreneurial Creativity and Innovation 33ellysazainudinNo ratings yet
- Nature and Development of EntrepreneurshipDocument33 pagesNature and Development of EntrepreneurshipEDERLYN DELOS REYESNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 - Part-2Document15 pagesUnit-2 - Part-2AnupriyaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Definitions of Entrepreneurship On The WebDocument18 pagesEntrepreneurship: Definitions of Entrepreneurship On The WebRohit HedaooNo ratings yet
- CS 5003 DBMS Unit IV Scanned Notes Part-IIIDocument26 pagesCS 5003 DBMS Unit IV Scanned Notes Part-IIIGourav Mandwal100% (1)
- Presentation 2 BMGT Understanding EntrepreneurshipDocument17 pagesPresentation 2 BMGT Understanding EntrepreneurshipMartin ChikumbeniNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial ManagementDocument17 pagesEntrepreneurial ManagementCasey AbelloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 3Document98 pagesChapter 1 - 3tot stephenNo ratings yet
- Eb 2022 2023Document87 pagesEb 2022 2023Ronald Pojo ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- What Is An EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesWhat Is An EntrepreneurshipIffat ZehraNo ratings yet
- Creativity and Innovation: Topic OneDocument16 pagesCreativity and Innovation: Topic Onesimi duttNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Development: Prepared and Presented By: Dr. Shuchi Goel Assistant Professor DME Management SchoolDocument58 pagesEntrepreneurship Development: Prepared and Presented By: Dr. Shuchi Goel Assistant Professor DME Management SchoolDevesh BalodhiNo ratings yet
- Creativity and Innovation: Entrepreneurship For Students Topic OneDocument16 pagesCreativity and Innovation: Entrepreneurship For Students Topic OneIndira SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1yashchotaliya.el21No ratings yet
- Ci 1Document16 pagesCi 1Wan QENo ratings yet
- ENF123 Lecture 2Document7 pagesENF123 Lecture 2Dave NNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Enter NewDocument31 pagesChapter One Enter Newyomif tamiruNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Bba (Tu) Sixth SemesterDocument42 pagesEntrepreneurship: Bba (Tu) Sixth Semesterbibukar jung karki100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Fundamentals of EntrepreneurshipDocument16 pagesLecture 1 Fundamentals of EntrepreneurshipKanana kimathiNo ratings yet
- Entreprunership Pharama AssigmDocument3 pagesEntreprunership Pharama Assigmsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship - IntroDocument36 pagesEntrepreneurship - IntroShweta GoelNo ratings yet
- Concept of Entrepreneur: UNIT 1: An Overview of EntrepreneurshipDocument15 pagesConcept of Entrepreneur: UNIT 1: An Overview of Entrepreneurshipnotes.mcpuNo ratings yet
- Entreprenureship 2 PDFDocument51 pagesEntreprenureship 2 PDFnotes.mcpuNo ratings yet
- Concept of Entrepreneur: UNIT 1: An Overview of EntrepreneurshipDocument15 pagesConcept of Entrepreneur: UNIT 1: An Overview of Entrepreneurshipnotes.mcpuNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship FinalsDocument32 pagesEntrepreneurship FinalsRussel Joseph DavaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship CH 1Document20 pagesEntrepreneurship CH 1AYELENo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and Small Business Management (Bme-212)Document240 pagesEntrepreneurship and Small Business Management (Bme-212)GemmeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Entrepreneurship M KaplanDocument7 pagesChapter 1-Entrepreneurship M KaplanShan EllahiNo ratings yet
- CH 1& 3 Modified The Nature of Entrepreneurship 2 2 2Document74 pagesCH 1& 3 Modified The Nature of Entrepreneurship 2 2 2jaabirnadiriiNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument19 pagesChapter OneBereket TarikuNo ratings yet
- Entreprenuership 1,2Document74 pagesEntreprenuership 1,2Fikiru DubaNo ratings yet
- Balaristha DoshaDocument4 pagesBalaristha DoshaAstroSunilNo ratings yet
- FEMADocument51 pagesFEMAChinmay Shirsat50% (2)
- Proforma Invoice - ConakryDocument1 pageProforma Invoice - ConakryAndy WeiNo ratings yet
- Business Standard 18th AugDocument11 pagesBusiness Standard 18th AugSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Curso Inglés Desde CERO - Nivel Básico - 21-25Document11 pagesCurso Inglés Desde CERO - Nivel Básico - 21-25david morrisonNo ratings yet
- Carnival Internet Package Price Up To 100 Mbps Speed Best Internet Provider 2Document1 pageCarnival Internet Package Price Up To 100 Mbps Speed Best Internet Provider 2Jahidul Hasan NumanNo ratings yet
- MABX 2014 Construction Buyers GuideDocument158 pagesMABX 2014 Construction Buyers Guidemabx_PANo ratings yet
- Consumer Reports Lesson Plan: Purchasing Products: VocabularyDocument10 pagesConsumer Reports Lesson Plan: Purchasing Products: VocabularyEmmanuel DianaNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra Stamp Act, 1958Document41 pagesMaharashtra Stamp Act, 1958ayushi agrawalNo ratings yet
- Ncert BookDocument14 pagesNcert Bookviswanathan periyasamyNo ratings yet
- Tapispisan Vs CA: 157950: June 8, 2005: J. Callejo SR: en Banc: DecisionDocument19 pagesTapispisan Vs CA: 157950: June 8, 2005: J. Callejo SR: en Banc: DecisionApay GrajoNo ratings yet
- Five Dials: Number 15Document49 pagesFive Dials: Number 15DouglasW822No ratings yet
- Spear v. Place, 52 U.S. 522 (1851)Document7 pagesSpear v. Place, 52 U.S. 522 (1851)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- 1968 Hypogene Texture and Mineral Zoning in A Copper Granodiorite Porphyry Stock NielsenDocument14 pages1968 Hypogene Texture and Mineral Zoning in A Copper Granodiorite Porphyry Stock NielsenKevin Hiram Torres Montana100% (1)
- Arts Q2 Module 3 FINAL1Document14 pagesArts Q2 Module 3 FINAL1halemahpacoteNo ratings yet
- Seab A-Level Lit H2 9725 - 2011Document34 pagesSeab A-Level Lit H2 9725 - 201127031993No ratings yet
- Incoterms For Beginners 1Document4 pagesIncoterms For Beginners 1Timur OrlovNo ratings yet
- Glo 20is 2017 PDFDocument317 pagesGlo 20is 2017 PDFKristine LlamasNo ratings yet
- RPS Energy Savings UpdateDocument9 pagesRPS Energy Savings UpdateinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Microhydro Myths & MisconceptionsDocument8 pagesMicrohydro Myths & Misconceptionscarra80No ratings yet