Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Osmo Regulation
Uploaded by
ashar sarbini0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views6 pagesOsmoregulation is the process by which the body regulates osmotic pressure through the production of antidiuretic hormone (ADH). Osmoreceptor cells in the hypothalamus monitor blood osmotic pressure. When the pressure increases, as from dehydration, the cells stimulate the pituitary gland to secrete more ADH. This causes kidneys to reabsorb more water and produce more concentrated urine, lowering osmotic pressure. When pressure decreases, as from overhydration, the cells secrete less ADH, kidneys reabsorb less water, and urine contains more water to raise osmotic pressure. This negative feedback loop maintains osmotic pressure within its normal range.
Original Description:
power point
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOsmoregulation is the process by which the body regulates osmotic pressure through the production of antidiuretic hormone (ADH). Osmoreceptor cells in the hypothalamus monitor blood osmotic pressure. When the pressure increases, as from dehydration, the cells stimulate the pituitary gland to secrete more ADH. This causes kidneys to reabsorb more water and produce more concentrated urine, lowering osmotic pressure. When pressure decreases, as from overhydration, the cells secrete less ADH, kidneys reabsorb less water, and urine contains more water to raise osmotic pressure. This negative feedback loop maintains osmotic pressure within its normal range.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views6 pagesOsmo Regulation
Uploaded by
ashar sarbiniOsmoregulation is the process by which the body regulates osmotic pressure through the production of antidiuretic hormone (ADH). Osmoreceptor cells in the hypothalamus monitor blood osmotic pressure. When the pressure increases, as from dehydration, the cells stimulate the pituitary gland to secrete more ADH. This causes kidneys to reabsorb more water and produce more concentrated urine, lowering osmotic pressure. When pressure decreases, as from overhydration, the cells secrete less ADH, kidneys reabsorb less water, and urine contains more water to raise osmotic pressure. This negative feedback loop maintains osmotic pressure within its normal range.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
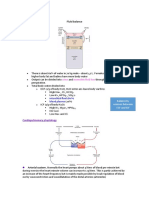
OSMOREGULATION
• - Osmoregulation is the regulation of osmotic pressure of tissue
fluid and blood at constant or near constant optimum level . This
is essential for body to function efficiently.
• - Carried out by hypothalamus and pituitary gland
• - Osmoregulation is achieved mainly by regulating the
volume of urine production and excretion from the
kidneys
• - This process is achieved a negative feedback mechanism
• - The hormone responsible for osmoregulation is the
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
• - ADH produced in hypothalamus and stored in posterior
pituitary gland before it is released in bloodstream
• - Osmoreceptor cells in the hypothalamus monitor the
blood osmotic pressure
• - Blood osmotic pressure increase when a person sweats a
lot during hot weather or drinks too little water
• - A decrease in blood volume occurs during haemorrhage
or severe dehydration
• - When water content falls below normal range , the
concentration of solutes in the blood increase and tis
causes an increase in blood osmotic pressure
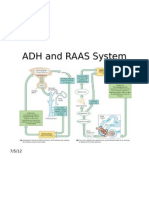
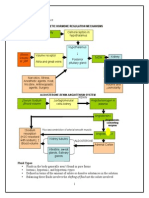
1) Drinks too much of water
Blood osmotic pressure decrease
below the normal range.
7) An increase in blood osmotic
pressure creates a negative
2) Osmoreceptor cells in the feedback in the hypothalamus
hypothalamus are less stimulated.
hypothalamus
3) The pituitary gland is less
6) The result is an increase
stimulated,less ADH is secreted
in the blood osmotic
from the pituitary gland Pituitary pressure and a return to the
gland normal range
Adrenal gland stimulated to
release aldosterone 5) This means less water is
reabsorbed from the filtrate into
4) The lower level of ADH the blood. As a result , urine
causes the distal convoluted contain more water and is lighter
tubule and collecting ducts to in colour
be less permeable to water
1) Drinks too little water
Blood osmotic pressure
increase above normal range
7) The lower the osmotic pressure creates a
negative feedback mechanism which reduces
the activity of the hypothalamic osmoreceptor
cells, which in turn, stop stimulating the
2) Osmoreceptor cells in the
pituitary gland to secrete more ADH
hypothalamus detect the increase in blood hypothalamus
osmotic pressure and are stimulated
6) The result is a decrease
3) Osmoreceptor cells in the in the blood osmotic
Pituitary
hypothalamus stimulate the pituitary gland pressure and a return to a
gland
to secrete more ADH into blood normal range
Adrenal gland is not stimulated
to release aldosterone
5) This means more water is
4) The higher level of ADH reabsorbed from the filtrate into the
causes the distal convoluted blood. Since more water content of the
tubule and collecting duct to urine decreases. Urine becomes more
be more permeable to water concentrated and darker in colour
You might also like
- BSN 1A Group 2 Urine Concentration Written Report PDFDocument10 pagesBSN 1A Group 2 Urine Concentration Written Report PDFgielduqueNo ratings yet
- 3.4-3.6 Coordination and ResponseDocument32 pages3.4-3.6 Coordination and ResponseathirahNo ratings yet
- Report Ko!!Document2 pagesReport Ko!!Angelica BrilloNo ratings yet
- General Biology PPT Darryl Arcillas & Dency TuastumbanDocument14 pagesGeneral Biology PPT Darryl Arcillas & Dency TuastumbanApril Rose Caquilala GalauraNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation: Grade 11 BiologyDocument12 pagesOsmoregulation: Grade 11 Biologysenpai ozhonNo ratings yet
- The Effect of ADH On Tubule Permeability and in Water Balance - HigherDocument2 pagesThe Effect of ADH On Tubule Permeability and in Water Balance - HigherLisa HendenNo ratings yet
- OSMOREGULATIONDocument16 pagesOSMOREGULATIONmacyhumairaNo ratings yet
- Surmacz Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance1Document20 pagesSurmacz Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance1leone shikukuNo ratings yet
- Posterior Pituitary: DR Axelle Saverettiar Mbbs Physiology Department SSR Medical CollegeDocument60 pagesPosterior Pituitary: DR Axelle Saverettiar Mbbs Physiology Department SSR Medical CollegeÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Osmoregulation NotesDocument2 pagesOsmoregulation NotesGood AstraNo ratings yet
- Negative Feedback Mechanism: (Renal Electrolyte System)Document4 pagesNegative Feedback Mechanism: (Renal Electrolyte System)Dip ThapaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 NCM 112Document4 pagesTopic 3 NCM 112Marielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailurePerry Oliver AlvarezNo ratings yet
- OsmoregulationDocument1 pageOsmoregulation11 Sci C2-P - Hervid Adolf Theodorus MangindaanNo ratings yet
- 2d) Patofisiologi Sesak Napas by Dr. AminuddinDocument39 pages2d) Patofisiologi Sesak Napas by Dr. AminuddinMUHAMMAD BAGIR ALJUFRINo ratings yet
- ShockDocument19 pagesShockIslam Atef SalamaNo ratings yet
- ADH and Mineralocorticoids RegulationDocument67 pagesADH and Mineralocorticoids RegulationSourabh NandaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document3 pagesQuiz 1Wiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Physiology Homeostatic Control and Starling ForcesDocument2 pagesPhysiology Homeostatic Control and Starling ForcesKaedehara KazuhaNo ratings yet
- Shock, Hypovolemic: Restoring Perfusion in Hypovolemic ShockDocument3 pagesShock, Hypovolemic: Restoring Perfusion in Hypovolemic Shockkarelly molinaNo ratings yet
- Control of The Body's Water ContentDocument3 pagesControl of The Body's Water ContentLADDER TIPSNo ratings yet
- Fluid & ElectrolytesDocument75 pagesFluid & ElectrolytesfaridahuNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument1 pageDiabetes InsipidusAnold ShangaliNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University Pathology Lecture on Hemodynamic DisordersDocument10 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University Pathology Lecture on Hemodynamic DisordersUshuaia Ira Marie L. GallaronNo ratings yet
- 1dasar Dasar Terapi Cairan PDFDocument23 pages1dasar Dasar Terapi Cairan PDFFitri ruli aslamahNo ratings yet
- 4 2 HomeworkDocument8 pages4 2 HomeworkShawntel IsordiaNo ratings yet
- Secretion of Potassium Ions Into The NephronDocument1 pageSecretion of Potassium Ions Into The NephronDoraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageMia PascualNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument105 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (3)
- DLC911 FeedbackDocument29 pagesDLC911 FeedbackJessecaNo ratings yet
- Fluids Electrolytes and Acid Base ImbalancesDocument8 pagesFluids Electrolytes and Acid Base ImbalancesSamantha Bernardo UndaNo ratings yet
- Leg Swelling Fluid Balance: Urine Insensible Fluid LossDocument9 pagesLeg Swelling Fluid Balance: Urine Insensible Fluid LossDarwithaNo ratings yet
- T5 Fluid and Fluid Imbalances PTPDocument4 pagesT5 Fluid and Fluid Imbalances PTPangela adelantarNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes ReviewerDocument4 pagesFluids and Electrolytes ReviewerdverraNo ratings yet
- The Role of Human Organ in HomeostasisDocument8 pagesThe Role of Human Organ in Homeostasisnozel77No ratings yet
- Physiology LAB - Blood - ReviewerDocument22 pagesPhysiology LAB - Blood - ReviewerRYABELLE JESUSA SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Iv FluidsDocument6 pagesIv FluidsCrishara PalomoNo ratings yet
- Biology class notesDocument11 pagesBiology class notessnnvcqzgnbNo ratings yet
- How Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?Document14 pagesHow Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?api-246259817No ratings yet
- 03 - Tissue Fluid & OedemaDocument38 pages03 - Tissue Fluid & Oedemashabnam sajidaNo ratings yet
- 2025 Module 5 Communication, Homeostasis and EnergyDocument41 pages2025 Module 5 Communication, Homeostasis and Energyharman panwarNo ratings yet
- Sistem Limfatik: M. Rasjad Indra Laboratorium Ilmu Faal Fk. UnibrawDocument24 pagesSistem Limfatik: M. Rasjad Indra Laboratorium Ilmu Faal Fk. UnibrawLuthfi HakimNo ratings yet
- Excretion 2 (Homeostasis)Document48 pagesExcretion 2 (Homeostasis)samskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 HomeostasisDocument8 pagesChapter 20 HomeostasisLisa AllisyaNo ratings yet
- Physio B 1.2 Renal Physiology Pt. 4 (Dr. Vila) : Because of Increase Water ReabsorptionDocument5 pagesPhysio B 1.2 Renal Physiology Pt. 4 (Dr. Vila) : Because of Increase Water ReabsorptionAnny AlvrzNo ratings yet
- Describe Long Term Regulation of Arterial Blood PressureDocument1 pageDescribe Long Term Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressurelinna chinNo ratings yet
- NEUROHIPOFISISDocument22 pagesNEUROHIPOFISISatik mayasariNo ratings yet
- SHOCK - HandoutsDocument6 pagesSHOCK - HandoutsKim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Feedback MechanismDocument25 pagesFeedback Mechanismkaloy domanaisNo ratings yet
- The Kidney Excretion and OsmoregulationDocument12 pagesThe Kidney Excretion and OsmoregulationLashaunte Hodge HobsonNo ratings yet
- ADH and RAAS SystemDocument12 pagesADH and RAAS SystemSyarif_shrfNo ratings yet
- FILE 20201125 231142 Hyponatremia A Practical ApproachDocument12 pagesFILE 20201125 231142 Hyponatremia A Practical ApproachTrọng ThuNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Water-Salt Metabolism: Prof. Oleksandr AtamanDocument35 pagesDisorders of Water-Salt Metabolism: Prof. Oleksandr AtamanZAKIA KHALID ALINo ratings yet
- IAL Biology SB2 Answers 7CDocument7 pagesIAL Biology SB2 Answers 7CsalmaNo ratings yet
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument18 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesAbby Trisha MadularaNo ratings yet
- PP24 Functioning of The KidneyDocument81 pagesPP24 Functioning of The KidneyLeloNo ratings yet
- NORCETDocument101 pagesNORCETDiksha DhillonNo ratings yet
- Fluid J Electrolyte J and Acid-Base BalanceDocument11 pagesFluid J Electrolyte J and Acid-Base Balancejeraldine marceraNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- ShirtDocument1 pageShirtashar sarbiniNo ratings yet
- Eseiform 3Document46 pagesEseiform 3norhanisa100% (1)
- No. Questions Pages Number 1. 1-5 2. 6-8 3. 9-10 4. 11-13 5. Further Explorations 14-17Document2 pagesNo. Questions Pages Number 1. 1-5 2. 6-8 3. 9-10 4. 11-13 5. Further Explorations 14-17ashar sarbiniNo ratings yet
- Terengganu K2 - 1Document23 pagesTerengganu K2 - 1admin nweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document6 pagesChapter 3ashar sarbiniNo ratings yet
- Add Math ProjectDocument18 pagesAdd Math Projectashar sarbiniNo ratings yet
- Endocrine, USMLE ENDPOINTDocument73 pagesEndocrine, USMLE ENDPOINTDaNy Chiriac50% (2)
- Essensial Hypertension Pathogenesis and PathophsiologyDocument22 pagesEssensial Hypertension Pathogenesis and PathophsiologyAmeliana KamaludinNo ratings yet
- Presented by - Yogesh Dengale 1 M.SC NursingDocument56 pagesPresented by - Yogesh Dengale 1 M.SC NursingalexjohnvtNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)Document7 pagesNCM 106 - Week 2 (Cardiovascular P1) (Midterm)MARIA KAWILANNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument52 pagesAntihypertensive Drugsapi-224264169No ratings yet
- Primary AldosteronismDocument5 pagesPrimary AldosteronismIfeanyichukwu OgbonnayaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Endocrine SystemDocument84 pagesDisorders of The Endocrine Systemcy lifeNo ratings yet
- Nephrology TestDocument112 pagesNephrology TestRapid Medicine50% (2)
- Disorders of Sodium and Potassium MetabolismDocument18 pagesDisorders of Sodium and Potassium MetabolismTukuWoNo ratings yet
- Fluid & ElectrolyteDocument26 pagesFluid & Electrolytesanjana bhatia100% (1)
- Maglumi 600Document4 pagesMaglumi 600mahmoud yaseen100% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument65 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalancesreenu100% (4)
- Disorders of The Adrenal GlandsDocument9 pagesDisorders of The Adrenal Glandsmoon businessNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis 121117100359 Phpapp02Document68 pagesHomeostasis 121117100359 Phpapp02midahrazalNo ratings yet
- Disease of Adrenal GlandDocument47 pagesDisease of Adrenal GlandgibreilNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 2 MCNDocument8 pagesPractice Test 2 MCNIriel Nadonga50% (2)
- Fluids and Electrolytes: Epidemiology/PathophysiologyDocument27 pagesFluids and Electrolytes: Epidemiology/PathophysiologyManna YankiNo ratings yet
- Physio ExDocument4 pagesPhysio ExNadifaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Answer KeyDocument10 pagesEndocrine Answer KeyJoyce LimNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Part 1Document131 pagesEndocrinology Part 1LucjaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument59 pagesEndocrine SystemCharm Angeles100% (3)
- HORMONES CONTROL DIGESTIONDocument5 pagesHORMONES CONTROL DIGESTIONAhmed OmaarNo ratings yet
- Hormones Secreted by Endocrine GlandsDocument5 pagesHormones Secreted by Endocrine Glandsaditya7324No ratings yet
- Lecture 20 Notes 2018Document6 pagesLecture 20 Notes 2018Omed ZarifiNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Fluid and Transfusion ManagementDocument52 pagesPerioperative Fluid and Transfusion ManagementIndah Fitri Okta100% (2)
- Addison's Disease: Symptoms, Causes, TreatmentDocument7 pagesAddison's Disease: Symptoms, Causes, TreatmentDexter DawsonNo ratings yet
- ADRENALSDocument60 pagesADRENALSJyoti ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document23 pagesChapter 16Richard RichardsNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading RSP Conn Syndrome Aulia PDFDocument33 pagesJournal Reading RSP Conn Syndrome Aulia PDFAhmad Nur AuliaNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument13 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesHenry Philip93% (15)