Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fruits and Veggies: 5 A Day: The Color Way
Uploaded by
Jeevajothy Satchithanandan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views32 pagesFruits and Vegetables for health
Original Title
Fruits and Veggies
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFruits and Vegetables for health
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
65 views32 pagesFruits and Veggies: 5 A Day: The Color Way
Uploaded by
Jeevajothy SatchithanandanFruits and Vegetables for health
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 32
Fruits and Veggies
5 A Day: the Color Way
5-a-day notes
Answer these questions in your notebook from
the presentation.
1. What are the nutrients and health benefits
in each of the 5 colors of fruits and
vegetables?
2. Name two sources each of vitamins C & E?
3. What is the difference between fruits and
vegetables?
4. What is the difference in scientists’ and
cooks’ definitions of fruits and vegetables?
5. Write down each of the 8 types of
vegetables and at least one
example of each.
5-a-day notes (cont.)
Answer these questions in your notebook from
the presentation.
6. Write down a buying and a storage tip for
vegetables.
7. Which convenience fruit or veggie do you
eat most often? What solution does the
presentation offer for that type?
8. Identify and define the 6 cutting
techniques described in the presentation.
9. Identify & define the 4 cooking methods
described for fruit.
10. Identify & define the 6 cooking
methods described for vegetables.
Varying our colors
Important to eat a variety each day
The different colors provide us with
different nutrients
Helps maintain a healthy weight, if
used as part of a low fat diet
Protects against aging
Reduces the risk of cancer and heart
disease.
Red
Contains the following nutrients:
Lycopene - An antioxidant that helps reduce
the risk of several types of cancer.
Anthocyanins - An anti-inflammatory that
helps protect blood health, the nervous system,
and prevent diabetes
Promotes a healthy heart
Memory function
Lowers risk of some cancers
Urinary tract health
Yellow/Orange
Contain the following nutrients:
Beta-carotene – an antioxidant that helps reduce the
risk of cancer, heart disease, maintains eyesight, and
helps boost the immune system.
Bioflavonoids – work with vitamin C to help reduce the
risk of cancer, strengthen bones, teeth, heal wounds,
keep skin healthy, and lower the risk of heart attacks.
Helps maintain:
A healthy heart
Vision health
A healthy immune system
White
Contains the following nutrient:
Allicin - which helps control blood pressure and
cholesterol and seems to increase the body's
ability to fight infection.
Helps maintain:
A healthy heart
Healthy cholesterol levels
A lower risk of some cancers
Green
Contains the following nutrients:
Lutein – an antioxidant that helps reduce the
risk of cataracts and macular degeneration.
Indoles – helps to reduce the risk of breast
and prostate cancer.
Helps maintain:
Vision health
A lower risk of some cancers
Strong bones and teeth
Blue/Purple
Contains the following nutrients:
Anthocyanins & phenols - antioxidants that
can help reduce the risk of cancer, heart
disease, and Alzheimer's and promote healthy
aging.
Helps maintain:
A lower risk of cancer
Urinary tract health
Memory function
Healthy aging
Nutrients in Fruits and
Vegetables
Low in fat and sodium
High in carbohydrates
High in antioxidants
Vitamin C: citrus fruits, but also kiwi,
strawberries, cantaloupe, cabbage, and potatoes
Vitamin E: apples and warm-weather fruits-
apricots, nectarines, peaches, and cruciferous
vegetables (in the cabbage family- help reduce
risk of cancer)
Beta Carotene (makes Vitamin A): yellow or
orange vegetables, cruciferous vegetables
Is it a fruit or vegetable?
Botanically-speaking (science of plants)
Fruits are reproductive organs
(ripened ovaries containing one or
many seeds),
Vegetables are vegetative organs
which sustain the plant.
Since “vegetable” is not a botanical
term, vegetables can also include:
leaves (lettuce),
stems (asparagus),
roots (carrots),
flowers (broccoli),
bulbs (garlic),
seeds (peas & beans),
botanical fruits such as cucumbers,
squash, pumpkins, & capsicums
(peppers)
Is it a fruit or vegetable?
Culinary-perspective
Here is where it gets tricky
If it is the fruit of the
plant & has seeds, it is a
fruit.
However, fruits, such as
tomatoes & cucumbers,
used in savoury cooking
are generally referred to
as vegetables.
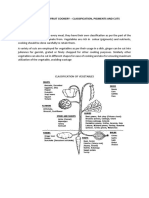
Types of Vegetables
Fruits: fruit of the plant
Cucumbers, eggplant,
tomatoes
Roots: underground
plant parts
Carrots, beets, turnips
Types of Vegetables
Stems: edible main
structure of plants
Celery, asparagus
Tubers: large underground
stem that stores nutrients
Potatoes
Types of Vegetables
Leaves: plant’s manufacturing
areas
Spinach, lettuce, and kale
Bulbs: layers or fleshy leaves
surround part of the stem
Onions and garlic
Types of Vegetables
Seeds: a small embryonic
plant enclosed in a seed coat
Corns, beans, and peas
Flowers: flower of the plant,
with stem, where seeds are
made.
Broccoli and cauliflower
Buying and Storing
buying storing
Inspect carefully Unripe fruits: place in
a paper bag at room
Look for bright color and
temperature
crispness
Do not line bottom of
Test for ripeness: press drawers with paper
gently, if it gives slightly, towels!!!! It causes
it is ripe molding.
For best quality buy in Potatoes and onions:
season cool, dark, dry place
Avoid decay and bruising Refrigerate in crisper
of fridge
Punch holes in plastic
bags
Convenience Fruits and Veggies
Canned, Frozen, and Dried
Challenges Solutions
Canned fruits are often Look for fruits packed in natural
high in added sugar. juice instead of sugar syrup.
Canned vegetables are Look for low-sodium varieties.
often high in sodium. Drain the liquid from the
vegetables before heating.
Some frozen vegetable are Buy frozen vegetables in bags.
relatively expensive. Buy plain vegetables without
sauces and other extras. Add
your own special touches, such
as a sprinkling of herbs.
Washing produce
Wash to remove dirt,
pesticides, and
pathogens
Wash just before use
Wash, even if you are
going to peel
Cutting Fresh Produce
Chiffonade: Finely cut strips or
ribbons or leafy vegetables or herbs.
Cutting Fresh Produce
Julienne: To cut into narrow, match-
like sticks
Cutting Fresh Produce
Mince: to cut into tiny pieces (garlic)
Cutting Fresh Produce
Chop: to cut foods into pieces; a
larger cut than dice or mince and not
uniform
Cutting Fresh Produce
Dice: a cube, usually of a vegetable,
that ranges from ¼ inch to ¾ inch
square
Cutting Fresh Produce
Slice: a thin, flat piece cut from
something
Cooking Fruits
Poaching or Stewing: cooking fruit
in enough liquid to cover it- aims to
keep the shape of the fruit
Fruit Sauces: cooking fruit into a
liquid (apples, plums, pears)
Cooking Fruits
Baking: Most often apples, need to
be cored, often seasoned before
baking
Microwaving: cooks quickly, keeps
fresh flavor and shape, be careful not
to overcook
Cooking Vegetables
Blanche: to
slightly precook
vegetables to kill
enzymes before
freezing
Saute: to cook in a
pan with a small
amount of hot fat.
Cooking Vegetables
Boil: To cook in
water or liquid at a
bubbling point
Simmer: to cook in
a liquid just below
boiling point
Cooking Vegetables
Steam: to cook over
boiling water-
minimizes vitamin
loss. Healthiest way to
cook vegetables.
Shock: Place cooked
vegetable in ice-cold
water to keep the
bright color and
crispness
References
http://www.ci.berkeley.ca.us/seniors/nutrition/
nutritionarchive/nutrition2004nov.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vegetable
http://www.fruitsandveggiesmorematters.org
http://www.ams.usda.gov/howtobuy/fveg.htm
You might also like
- On This Page:things To RememberDocument7 pagesOn This Page:things To RememberhamzaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 12Document17 pagesPresentation 12Sche ImdanNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Part-1: Nutritional and Medicinal Value: Nutritional and Medicinal ValueFrom EverandVegetable Part-1: Nutritional and Medicinal Value: Nutritional and Medicinal ValueNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Food and HealthDocument19 pagesUnit 1 Food and Healthk2bt65dghfNo ratings yet
- Fruits & VegetablesDocument24 pagesFruits & VegetablesSai CampbellNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Iloilo Science and Technology UniversityDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Iloilo Science and Technology UniversityKate Ashley MuedaNo ratings yet
- Vegetables and Vegetables CookeryDocument5 pagesVegetables and Vegetables CookeryRheccaNo ratings yet
- How Vegetables are Classified by Plant PartsDocument12 pagesHow Vegetables are Classified by Plant PartsDanica SoriaNo ratings yet
- Cookery 10 Quarter 2 m1Document37 pagesCookery 10 Quarter 2 m1Jennifer CarpioNo ratings yet
- Fruits and VegetablesDocument16 pagesFruits and Vegetablescarlo jay evardoneNo ratings yet
- l2 Quarter 2 Week 1 - Prepare Mise en PlaceDocument38 pagesl2 Quarter 2 Week 1 - Prepare Mise en PlaceGwyneth VicenteNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1 VEGETABLES DISHES PERFORM MISE EN PLACEDocument137 pagesWEEK 1 VEGETABLES DISHES PERFORM MISE EN PLACERaeNo ratings yet
- Learning Module No. 6Document6 pagesLearning Module No. 6Christine Marie BoncalesNo ratings yet
- Informationsheet Cookery10.ADocument5 pagesInformationsheet Cookery10.Amarilyn bristolNo ratings yet
- Informationsheet Cookery10.ADocument5 pagesInformationsheet Cookery10.Amarilyn bristolNo ratings yet
- Preparing Vegetables DishesDocument38 pagesPreparing Vegetables DishesRica JosephinaNo ratings yet
- Reprt in TVLDocument29 pagesReprt in TVLriejinesaldivar250No ratings yet
- Eat Vegetables and Fruits - Canada's Food GuideDocument4 pagesEat Vegetables and Fruits - Canada's Food GuideMateo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Fruit and VegetablesDocument5 pagesFruit and VegetablesclaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Prepare Vegetable Dishes Tlte10Document5 pagesLesson 1 Prepare Vegetable Dishes Tlte10Kimby VentuzoNo ratings yet
- WHLP Cookery 10 q2w1Document6 pagesWHLP Cookery 10 q2w1Sean Thomas Kurt RoblesNo ratings yet
- Fruit and Vegetable Process Tecnology Chapter 3Document89 pagesFruit and Vegetable Process Tecnology Chapter 3robel kassawNo ratings yet
- Q2 Guide 1Document4 pagesQ2 Guide 1Gerald EscobalNo ratings yet
- 10 Cookery ReviewerDocument18 pages10 Cookery Reviewerferlynmae.bautista528No ratings yet
- Fruits and VegetablesDocument13 pagesFruits and Vegetablesg77barnesNo ratings yet
- TLE-031-Module 6Document10 pagesTLE-031-Module 6Jing KhaiNo ratings yet
- HE REVIEWERDocument14 pagesHE REVIEWERxls.cineNo ratings yet
- COOKERY 10 Quarter 2 LAS No. 1Document9 pagesCOOKERY 10 Quarter 2 LAS No. 1Chema PacionesNo ratings yet
- Cookery 2nd QuarterDocument26 pagesCookery 2nd QuarterJOHN LESTER BOTORNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Vegetable and Fruit CookeryDocument8 pagesUnit 6 Vegetable and Fruit CookeryKMCTCOLLEGEOFHOTELMANAGEMENT ANDCATERINGTECHNOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Classification of Vegetables:: 1. TubersDocument4 pagesClassification of Vegetables:: 1. TubersmichelleNo ratings yet
- Prepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesDocument60 pagesPrepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesAlodie Dela Raiz Asuncion89% (9)
- Self-Paced Lesson Plan PDFDocument6 pagesSelf-Paced Lesson Plan PDFRonakd MyaNo ratings yet
- Low-Income Produce Presentation FinalDocument25 pagesLow-Income Produce Presentation Finalapi-554351240No ratings yet
- TLE Cookery 10 2nd Grading ReviewersDocument5 pagesTLE Cookery 10 2nd Grading ReviewersWilma AmliwNo ratings yet
- Tle 10 Mise en PlaceDocument38 pagesTle 10 Mise en PlaceEdmark RosalesNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 CookeryDocument18 pagesMODULE 1 CookeryMaribel B GarciaNo ratings yet
- VegetablesDocument20 pagesVegetablesJada KnightsNo ratings yet
- Is Your Food What: ? ColorDocument8 pagesIs Your Food What: ? ColorEyog VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Fruit Versus VegetableDocument4 pagesFruit Versus VegetableReezvee Sultana EvaNo ratings yet
- Fruits and Vegetable LessonDocument5 pagesFruits and Vegetable LessonRuby Esmeralda AndayaNo ratings yet
- Prepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesDocument120 pagesPrepare Vegetable and Seafood DishesJoeven Pantaleon67% (3)
- How To Eat HealthyDocument17 pagesHow To Eat Healthymosraining92No ratings yet
- Anti Inflammatory DietDocument6 pagesAnti Inflammatory DietHW GomarNo ratings yet
- Fruits and VegetablesDocument2 pagesFruits and Vegetableshoussemtlili20182019No ratings yet
- Hargrove Davis Perry NewsletterDocument4 pagesHargrove Davis Perry Newsletterapi-268567153No ratings yet
- TLE ReviewerDocument8 pagesTLE ReviewerAndrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document27 pagesModule 9Camille MalvecinoNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Prepare Vegetable DishesDocument9 pagesModule 7 Prepare Vegetable DishesGilbert LoredoNo ratings yet
- Tle 1Document6 pagesTle 1Soleil RiegoNo ratings yet
- Fruits and VegetablesDocument35 pagesFruits and VegetablesAvegael PedregosaNo ratings yet
- VEGETABLESDocument60 pagesVEGETABLESAaliyah CarlobosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Prepare Vegetable DishesDocument108 pagesLesson 1 Prepare Vegetable DishesRonald Serrano100% (3)
- Tle 10 q2 Week 1-2Document8 pagesTle 10 q2 Week 1-2Joebell PadillaNo ratings yet
- PDF Peru Seguridad CiudadanaDocument69 pagesPDF Peru Seguridad CiudadanaAngel Daniel Supo TiconaNo ratings yet
- Eat by Color by DR David HeberDocument11 pagesEat by Color by DR David HeberCaraNo ratings yet
- Final Cookery12 Q2 Module 2Document18 pagesFinal Cookery12 Q2 Module 2Junah SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Gayatri Japam Benefits Faster SandhyavandanamDocument17 pagesGayatri Japam Benefits Faster SandhyavandanamJeevajothy SatchithanandanNo ratings yet
- Importance of BreathingpranayamaDocument81 pagesImportance of BreathingpranayamaJeevajothy SatchithanandanNo ratings yet
- Raja Yoga InduismDocument26 pagesRaja Yoga Induismpalani22100% (3)
- Soap: Making Everyday Chemistry Public: Jump ToDocument11 pagesSoap: Making Everyday Chemistry Public: Jump ToJeevajothy SatchithanandanNo ratings yet
- THE SUPER SCIENCE OF GAYATRI - by Shriram Sharma AcharyaDocument177 pagesTHE SUPER SCIENCE OF GAYATRI - by Shriram Sharma AcharyaGuiding Thoughts- Books by Pandit Shriram Sharma Acharya100% (10)
- Thinkonomics E-BookDocument56 pagesThinkonomics E-BookMsKNHunt100% (10)
- Whybook Animal Do Not Get Heart Attack Intro PDFDocument7 pagesWhybook Animal Do Not Get Heart Attack Intro PDFJeevajothy SatchithanandanNo ratings yet
- THE SUPER SCIENCE OF GAYATRI - by Shriram Sharma AcharyaDocument177 pagesTHE SUPER SCIENCE OF GAYATRI - by Shriram Sharma AcharyaGuiding Thoughts- Books by Pandit Shriram Sharma Acharya100% (10)
- 14 Self Treatment Hand Positions GuideDocument1 page14 Self Treatment Hand Positions GuideJeevajothy SatchithanandanNo ratings yet
- David Allen The Power of I AmDocument127 pagesDavid Allen The Power of I AmJj Zhang94% (18)
- MFRS - 116 PpeDocument26 pagesMFRS - 116 PpeJeevajothy Satchithanandan100% (3)
- Correct Prayer As Described by Neville GoddardDocument11 pagesCorrect Prayer As Described by Neville Goddardjupator50% (2)
- Reference Crystal HealingDocument8 pagesReference Crystal HealingcroangelNo ratings yet
- Dividend PolicyDocument50 pagesDividend PolicyJeevajothy SatchithanandanNo ratings yet
- Lobsang Rampa - Chapters of LifeDocument214 pagesLobsang Rampa - Chapters of LiferockstarlkNo ratings yet
- Healthy Living EbookDocument57 pagesHealthy Living EbookJeevajothy SatchithanandanNo ratings yet
- All These Things AddedDocument39 pagesAll These Things AddedJeevajothy SatchithanandanNo ratings yet
- Health Is FreeDocument16 pagesHealth Is FreeProf. MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Learning Models KohlerDocument19 pagesCognitive Learning Models KohlerJeevajothy SatchithanandanNo ratings yet
- Motivation - Healing Throught - The Power of Positive ThinkingDocument27 pagesMotivation - Healing Throught - The Power of Positive ThinkingkvsudheendraNo ratings yet
- Department of Education School Form 8 Learner's Basic Health and Nutrition Report (SF8)Document12 pagesDepartment of Education School Form 8 Learner's Basic Health and Nutrition Report (SF8)Jeff HambreNo ratings yet
- PN0621 CF1 ClinicalApproachDementiaDocument5 pagesPN0621 CF1 ClinicalApproachDementiaSwayang Sudha PandaNo ratings yet
- ERYTHRASMA PPT - PPTX ED - PPTX MDocument22 pagesERYTHRASMA PPT - PPTX ED - PPTX MAmmar HasyimNo ratings yet
- (ACV-S05) Quiz - Health & Wellness - INGLES IV (11935)Document3 pages(ACV-S05) Quiz - Health & Wellness - INGLES IV (11935)Erika Rosario Rodriguez CcolqqueNo ratings yet
- PEH 11 Q3 Mod1 Week 1 2 MELC01 Thelma R. SacsacDocument16 pagesPEH 11 Q3 Mod1 Week 1 2 MELC01 Thelma R. Sacsaccalvin adralesNo ratings yet
- PSW Weclome LetterDocument5 pagesPSW Weclome LetterMallius AllerisNo ratings yet
- First Aid and Water SurvivalDocument18 pagesFirst Aid and Water Survivalmusubi purpleNo ratings yet
- Apollo Munich Optima Restore Premium ReceiptDocument17 pagesApollo Munich Optima Restore Premium ReceiptParag AmbreNo ratings yet
- Passive Smoking PDFDocument69 pagesPassive Smoking PDFjeffrey domosmogNo ratings yet
- Ah102 Syllabus 20180417lDocument7 pagesAh102 Syllabus 20180417lapi-399629502No ratings yet
- Willingness To Pay For Improved Health Walk On The Accra-Aburi Mountains Walkway in GhanaDocument9 pagesWillingness To Pay For Improved Health Walk On The Accra-Aburi Mountains Walkway in GhanaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Tumor StagingDocument9 pagesTumor Stagingmalaran.deboraheloisaNo ratings yet
- Hormone Therapy IfmDocument16 pagesHormone Therapy IfmRamy LasheenNo ratings yet
- EVS - CO-5 - PPT - UO 5fDocument22 pagesEVS - CO-5 - PPT - UO 5fGirish KhedikarNo ratings yet
- Traffic Rules LiteracyDocument11 pagesTraffic Rules LiteracyMaricel AycoNo ratings yet
- Local Honey Might Help Your AllergiesDocument3 pagesLocal Honey Might Help Your AllergiesDaniel JadeNo ratings yet
- HFpEF Management 2023Document10 pagesHFpEF Management 2023ctsakalakisNo ratings yet
- RM NCC RN 8.0 CHP 21Document21 pagesRM NCC RN 8.0 CHP 21LonaBrochenNo ratings yet
- DNP 2021 A Women Justice Legal NeedsDocument20 pagesDNP 2021 A Women Justice Legal Needsdito1972No ratings yet
- Common mental health problems screeningDocument5 pagesCommon mental health problems screeningSaralys MendietaNo ratings yet
- Back From The Bluez - 09 - Self ManagementDocument5 pagesBack From The Bluez - 09 - Self ManagementMelanie DovaleNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Risk Factors Causes of Occupational Accidents in The Vocational SchoolDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Risk Factors Causes of Occupational Accidents in The Vocational Schooldesheila andariniNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Evaluation ChecklistDocument7 pagesPreoperative Evaluation ChecklistPiny Elleine CesarNo ratings yet
- Reaction To Frustration TestDocument7 pagesReaction To Frustration TestRushikesh MaidNo ratings yet
- BP FluorideTherapyDocument4 pagesBP FluorideTherapyKavana SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Eneza Ujumbe: The Voices of Mathare YouthDocument4 pagesEneza Ujumbe: The Voices of Mathare YouthakellewagumaNo ratings yet
- Ocean Breeze Air Freshener: Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesOcean Breeze Air Freshener: Safety Data SheetMark DunhillNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Physical AssessmentDocument6 pagesCardiovascular System Physical Assessmentpulsating humNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Functional Pain Score by Comparing To Traditional Pain ScoresDocument7 pagesAssessment of Functional Pain Score by Comparing To Traditional Pain ScoresKepompong KupukupuNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Heirloom Kitchen: Heritage Recipes & Family Stories from the Tables of Immigrant WomenFrom EverandHeirloom Kitchen: Heritage Recipes & Family Stories from the Tables of Immigrant WomenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Proteinaholic: How Our Obsession with Meat Is Killing Us and What We Can Do About ItFrom EverandProteinaholic: How Our Obsession with Meat Is Killing Us and What We Can Do About ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Not That Fancy: Simple Lessons on Living, Loving, Eating, and Dusting Off Your BootsFrom EverandNot That Fancy: Simple Lessons on Living, Loving, Eating, and Dusting Off Your BootsNo ratings yet
- Saved By Soup: More Than 100 Delicious Low-Fat Soups To Eat And Enjoy Every DayFrom EverandSaved By Soup: More Than 100 Delicious Low-Fat Soups To Eat And Enjoy Every DayRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Glucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingFrom EverandGlucose Goddess Method: A 4-Week Guide to Cutting Cravings, Getting Your Energy Back, and Feeling AmazingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (59)
- Plant Based Main Dishes Recipes: Beginner’s Cookbook to Healthy Plant-Based EatingFrom EverandPlant Based Main Dishes Recipes: Beginner’s Cookbook to Healthy Plant-Based EatingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Binging with Babish: 100 Recipes Recreated from Your Favorite Movies and TV ShowsFrom EverandBinging with Babish: 100 Recipes Recreated from Your Favorite Movies and TV ShowsNo ratings yet
- The All-American Cowboy Cookbook: Over 300 Recipes from the World's Greatest CowboysFrom EverandThe All-American Cowboy Cookbook: Over 300 Recipes from the World's Greatest CowboysNo ratings yet
- Sweetie Pie's Cookbook: Soulful Southern Recipes, from My Family to YoursFrom EverandSweetie Pie's Cookbook: Soulful Southern Recipes, from My Family to YoursRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Plant Based Sauces and Dips Recipes: Beginner’s Cookbook to Healthy Plant-Based EatingFrom EverandPlant Based Sauces and Dips Recipes: Beginner’s Cookbook to Healthy Plant-Based EatingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Pasta, Pretty Please: A Vibrant Approach to Handmade NoodlesFrom EverandPasta, Pretty Please: A Vibrant Approach to Handmade NoodlesNo ratings yet
- The Dude Diet: Clean(ish) Food for People Who Like to Eat DirtyFrom EverandThe Dude Diet: Clean(ish) Food for People Who Like to Eat DirtyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- The Fresh Eggs Daily Cookbook: Over 100 Fabulous Recipes to Use Eggs in Unexpected WaysFrom EverandThe Fresh Eggs Daily Cookbook: Over 100 Fabulous Recipes to Use Eggs in Unexpected WaysNo ratings yet
- Plant Based Salads and Wraps Recipes: Beginner’s Cookbook to Healthy Plant-Based EatingFrom EverandPlant Based Salads and Wraps Recipes: Beginner’s Cookbook to Healthy Plant-Based EatingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (20)
- Start Simple: Eleven Everyday Ingredients for Countless Weeknight MealsFrom EverandStart Simple: Eleven Everyday Ingredients for Countless Weeknight MealsNo ratings yet
- Tacos, Tortas, And Tamales: Flavors from the Griddles, Pots, and Streetside Kitchens of MexicoFrom EverandTacos, Tortas, And Tamales: Flavors from the Griddles, Pots, and Streetside Kitchens of MexicoNo ratings yet
- Weber's Ultimate Grilling: A Step-by-Step Guide to Barbecue GeniusFrom EverandWeber's Ultimate Grilling: A Step-by-Step Guide to Barbecue GeniusRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Wine Girl: The Obstacles, Humiliations, and Triumphs of America's Yougest SommelierFrom EverandWine Girl: The Obstacles, Humiliations, and Triumphs of America's Yougest SommelierRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (26)
- Keto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleFrom EverandKeto Friendly Recipes: Easy Keto For Busy PeopleRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- A Taste of Cowboy: Ranch Recipes and Tales from the TrailFrom EverandA Taste of Cowboy: Ranch Recipes and Tales from the TrailRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Plant Based Gluten Free Recipes: Beginner’s Cookbook to Healthy Plant-Based EatingFrom EverandPlant Based Gluten Free Recipes: Beginner’s Cookbook to Healthy Plant-Based EatingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)