Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ship History Wood
Uploaded by
tvkbhanuprakash0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views8 pagesHistory of Wooden Ships PPT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHistory of Wooden Ships PPT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views8 pagesShip History Wood
Uploaded by
tvkbhanuprakashHistory of Wooden Ships PPT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
श्री गणेशाय नमः
श्री कृष्णं वन्दे जगद्गुरुम्
जै हिन्द्
SSDSV
Prof. Bhanuprakash Tallapragada
Dept of Marine Engineering
College of Engineering (A)
Andhra University
Visakhapatnam - 530003
1. The first known vessels date back about 10,000 years ago,
but could not be described as ships. The first navigators
began to use animal skins or woven fabrics as sails. Affixed
to the top of a pole set upright in a boat, these sails gave
early ships range.
1. By around 3000 BC, Egyptians knew how to assemble
wooden planks into a hull. They used woven straps to lash
the planks together, and reeds or grass stuffed between
the planks helped to seal the seams.
1. The Egyptians were perfectly at ease building sailboats.
A remarkable example was a vessel 143 feet (44 m)
1. It is known that ancient Nubia/Axum traded with India, and
there is evidence that ships from Northeast Africa may have
sailed back and forth between India/Sri Lanka and Nubia
trading goods and even to Persia, and Rome.[19]
2. The oldest discovered sea faring hulled boat is the Late
Bronze Age Uluburun shipwreck off the coast of Turkey,
dating back to 1300 BC.
3. Before the introduction of the compass, celestial navigation
was the main method for navigation at sea. In China, early
versions of the magnetic compass were being developed
and used in navigation between 1040 and 1117.
1. The true mariner's compass, using a pivoting needle in a
dry box, was developed in Europe no later than 1300.
2. At this time, ships were developing in Asia in much the
same way as Europe. Japan used defensive naval
techniques in the Mongol invasions of Japan in 1281.
3. During the 15th century, China's Ming dynasty assembled
one of the largest and most powerful naval fleets in the
world for the diplomatic and power projection voyages
1. Elsewhere in Japan in the 15th century, one of the world's
first iron-clads, literally meaning "iron ships" was also
developed.
2. In Japan, during the Sengoku era from the fifteenth to 17th
century, the great struggle for feudal supremacy was
fought, in part, by coastal fleets of several hundred boats.
Korea, in the early 15th century built the "turtle ship", is
recognized as the first armored ship in the world.
3. Parallel to the development of warships, ships in service of
marine fishery and trade also developed in the period
between antiquity and the Renaissance.
1. During the first half of the 18th century, the French Navy
began to develop a new type of vessel known as a ship of
the line, featuring seventy-four guns.
2. This type of ship became the backbone of all European
fighting fleets. These ships were 56 metres (184 ft) long
and their construction required 2,800 oak trees and 40
kilometres (25 mi) of rope; they carried a crew of about
800 sailors and soldiers.
3. Ship designs stayed fairly unchanged until the late 19th
century.
1. The industrial revolution, new mechanical methods of
propulsion, and the ability to construct ships from metal
triggered an explosion in ship design. In 2007, the world's
fleet included 34,882 commercial vessels with gross tonnage
of more than 1,000 tons,totaling 1.04 billion tons.
2. In 2002, there were 1,240 warships operating in the world,
not counting small vessels such as patrol boats.
3. The size of the world's fishing fleet is more difficult to
estimate. The largest of these are counted as commercial
vessels, but the smallest are legion. Fishing vessels can be
found in most seaside villages in the world.
You might also like
- Understanding Ship Resistance and Propulsion ComponentsDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Ship Resistance and Propulsion ComponentstvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Understanding Ship Resistance and Propulsion ComponentsDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Ship Resistance and Propulsion ComponentstvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- ProfTVKB Propulsion Lect 01Document39 pagesProfTVKB Propulsion Lect 01tvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Proftvkb HW 10 Chap 03 ADocument1 pageProftvkb HW 10 Chap 03 AtvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- TVKB - Model Ship ExtrapolationDocument32 pagesTVKB - Model Ship ExtrapolationtvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Propeller & Propulsion Terminology: 1. DiameterDocument18 pagesPropeller & Propulsion Terminology: 1. DiametertvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Propeller TheoryDocument37 pagesChapter 3 Propeller TheorytvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- TVKB - Model Ship ExtrapolationDocument32 pagesTVKB - Model Ship ExtrapolationtvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- ProfTVKB - Transverse Wave InterferenceDocument15 pagesProfTVKB - Transverse Wave InterferencetvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- ProfTVKB - Propeller Geometry HWDocument1 pageProfTVKB - Propeller Geometry HWtvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Prof - TVKB Carlton Propeller 02Document26 pagesProf - TVKB Carlton Propeller 02tvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Propeller Geometry: Frames of ReferenceDocument14 pagesPropeller Geometry: Frames of ReferencetvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Q1) The Force Has A Magnitude of 5oon. Express F As A Vector in Terms of Unit Vectors I and J. Identify The X and Y Scalar Components of FDocument2 pagesQ1) The Force Has A Magnitude of 5oon. Express F As A Vector in Terms of Unit Vectors I and J. Identify The X and Y Scalar Components of FtvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Dimensional Analysis, Similitude, and ModelingDocument42 pagesFluid Mechanics: Dimensional Analysis, Similitude, and ModelingtvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- TVKB Rules of SraddhaDocument5 pagesTVKB Rules of SraddhatvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- TVKB Memh 2 Dof Lect 2Document16 pagesTVKB Memh 2 Dof Lect 2tvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Solid MechanicsDocument25 pagesSolid MechanicstvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Homework 6-7-2012Document4 pagesHomework 6-7-2012tvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Sri Bhagavad Git As 023394 MBPDocument237 pagesSri Bhagavad Git As 023394 MBPtvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- 120 Upanishads With Original Sanskrit TextsDocument679 pages120 Upanishads With Original Sanskrit TextsDr. Prashan Kumar Thakur100% (1)
- Circulation TheoryDocument23 pagesCirculation TheorytvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- TVKB Memh 2 Dof Lect 2Document16 pagesTVKB Memh 2 Dof Lect 2tvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Prof TVKB Propeller TheoryDocument26 pagesProf TVKB Propeller TheorytvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- TVKB R&P HM MethodDocument42 pagesTVKB R&P HM MethodtvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics DynamicsDocument39 pagesEngineering Mechanics Dynamicstvkbhanuprakash100% (1)
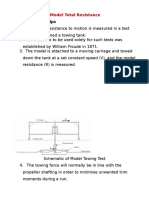
- Model Test Towing TankDocument29 pagesModel Test Towing Tanktvkbhanuprakash100% (1)
- TVKB Memh 2 Dof Lect 1Document21 pagesTVKB Memh 2 Dof Lect 1tvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- Intro To TurbulenceDocument21 pagesIntro To TurbulencetvkbhanuprakashNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- FPSO Hystory Old&NewDocument31 pagesFPSO Hystory Old&NewDaniel Mihailescu100% (3)
- Strength, Construction and Watertight SubdivisionDocument28 pagesStrength, Construction and Watertight SubdivisionBill Erick CastilloNo ratings yet
- The Cruise Industry PDFDocument53 pagesThe Cruise Industry PDFBrian Castañeda100% (1)
- Bill of LadingDocument17 pagesBill of LadingYuvraj SamantNo ratings yet
- Interview Application FormDocument11 pagesInterview Application FormANKIT POONIA100% (1)
- Beneteau 50 Owner's ManualDocument43 pagesBeneteau 50 Owner's ManualGrife Moda PraiaNo ratings yet
- 03 BulkheadDocument9 pages03 BulkheadLucky BoatNo ratings yet
- Tanker World Scale IndexDocument1 pageTanker World Scale IndexD-pacNo ratings yet
- Chartering AbrevationsDocument13 pagesChartering AbrevationsJuan ManuelNo ratings yet
- Notes For Phase IIDocument104 pagesNotes For Phase IISippu SifathullahNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment - PDF (Cargo Work)Document14 pagesHome Assignment - PDF (Cargo Work)Mitanshu ChadhaNo ratings yet
- 1.8 MaritimeenglishDocument3 pages1.8 MaritimeenglishAlief Syahreza DavinciNo ratings yet
- Lessons from the Titanic: Safety ReformsDocument3 pagesLessons from the Titanic: Safety ReformsammaramsyarNo ratings yet
- CV PelautDocument1 pageCV Pelautyogi smileNo ratings yet
- Baku Shipyard Company ProfileDocument14 pagesBaku Shipyard Company ProfileSarfaraz PatelNo ratings yet
- 2007 Rolls Royce Propulsion ProductsDocument24 pages2007 Rolls Royce Propulsion ProductsFlo MarineNo ratings yet
- Bb-02.final Drawing ListDocument21 pagesBb-02.final Drawing ListАлександр Королёв0% (1)
- M/V Wedellsborg: General Information Dimensions CranesDocument2 pagesM/V Wedellsborg: General Information Dimensions CranesDavephilsNo ratings yet
- Igf Vessels Cop DG CircularDocument5 pagesIgf Vessels Cop DG CircularAdrian Fernandes100% (1)
- Requirements on Carriage of PublicationsDocument5 pagesRequirements on Carriage of PublicationsSanket MahajanNo ratings yet
- Chartering and Brokerin Freighr Revenue CalculationDocument7 pagesChartering and Brokerin Freighr Revenue CalculationDeck OfficerNo ratings yet
- Vessel Class ListingDocument206 pagesVessel Class ListingLaurentiuMarianNo ratings yet
- Annexure Part-6 For English Application (Pgs From 93 To 108)Document20 pagesAnnexure Part-6 For English Application (Pgs From 93 To 108)Sayeem MuneerNo ratings yet
- EEXI Explained NKDocument36 pagesEEXI Explained NKGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic and Intact Stability Analysis For A Surface ShipDocument0 pagesHydrostatic and Intact Stability Analysis For A Surface ShipmedievoloNo ratings yet
- Technical Specs - MV PSV2 - REV01Document2 pagesTechnical Specs - MV PSV2 - REV01Syed Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Allotment of Indos No.: Pre Sea TrainingDocument3 pagesApplication Form For Allotment of Indos No.: Pre Sea TrainingChetan ChavanNo ratings yet
- Marine Survey Practice - Surveyor Guide Notes For Bulk Carriers SurveyDocument6 pagesMarine Survey Practice - Surveyor Guide Notes For Bulk Carriers SurveyJuanjo MarengoNo ratings yet
- CURRICULUM VITA FOR OILER POSITIONDocument1 pageCURRICULUM VITA FOR OILER POSITIONMuhammad Taufiq AmrullahNo ratings yet
- ExxonMobil Safety Criteria 2017 (Ocean Going Tanker)Document59 pagesExxonMobil Safety Criteria 2017 (Ocean Going Tanker)G_ARVALIS8470100% (8)