Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Odarp PradzOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Odarp PradzCopyright:
Available Formats
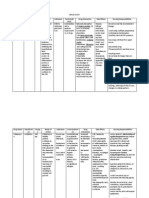
Drug Name Furosemide Lasix 40mg OD y
Action Potent loop diuretics that inhibit NaCl reabsorption at the proximal and distal tubules and ascending loop of henle. Promotes water and sodium excretion. y y
Indication Edema Hypercalemia y
Contraindication Contraindicated in patient with hypersensitivity to drug or any of its componentsin those with anuria. Use continuosly in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Patient with allergy to sulphonamides may also be allergic to furosemide.
Side Effects CNS: Fever, vertigo, headech, dizziness, weaknkess CV: Orthostatic hypotension, thrombophlebitis, volume depletion and dehydration. EENT: transient deafness (with too rapid IV injection) blurred or yellow vision. GI: pancreatitis, anorexia, abd l discomfort, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, constipation. GU: azotemia, nocturia, polyuria, frequent urination, oliguria. METABOLIC: asymptomatic hyperuvicemia, hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance, hypochloremic alkalosis, hypokalemia, F & C imbalance. y Hyponatremia y Hypocalcemia y Hypomagnesemia Musculoskeletal: Muscle spasm Skin: Dermatitis, purpura, photosensitivity
Nursing responsibility 1. Advise patient to stand slowly to prevent dizziness, not to drink alcohol, and to minimize strenuous exercise in hot weather. Instruct patient to report ringing in ears, severe abdominal pain, or sore throat and fever because they may indicate toxicity. Give P.O. or I.M. dose in the morning to prevent nocturia. Store tablet in light resistant container to prevent discoloration. Don t use yellow injectable preparation. If oliguria or azotemia develops or increase, notify prescriber.
2.
3.
4.
5.
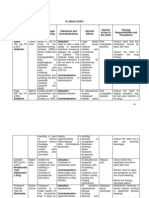
Drug Name Lactulose Rilax 30cc HS y y
Action Disaccharide laxative Produce osmotic effects on colon. Resulting distension promote peristalsis. Decreases blood ammonia build up that cause hepatic encephalopathy, probably as result of b acterial degradation which lowers PH of colon contents. y
Indication Constipation; prevent and treat hepatic encephalopathy, including hepatic precoma and coma in patient and severe hepatic disorder. To induce bowel movement evacuation in geriatric patient the colonic retention of barium and severe constipation after a barium meal examination. To restore bowel movements after hemorhoidectom y. y
Contraindication Contraindicated to patient with low galactose diet. Use cautiously in patient with DM because drug contains lactose, galactose & other sugars.
Side Effects GI: Abdominal cramps, belching, diarrhea, distention, flactulose, nausea, vomiting.
Nursing responsibility 1. Assess patients condition before starting their therapy and regularly after to monitor the drugs effectiveness. If patient has hepatic encephalopathy, assess mental condition. Monitor electrolyte levels potassium with long term use. Monitor ammonia levels in patient with hepatic disease. Replacement of fluid loss. To minimize sweet taste, dilute with water or fruit juice or give with food. Diarrhea may indicate overdose. Store at room temperature, 30oC DON T freeze.
2.
3.
4. 5.
6.
7.
Drug Name Spironolactone Aldactone 25mg tab OD y y
Action Potassium sparing diuretic. Antagonize aldosterone in distal tubule. Promotes water and sodium excretion and hinders potassium excretion, lowers BP and helps to diagnose primary hyperaldosteronism. y
Indication Essenital HPN, edema, CHF, liver cirrhosis, nephritic syndrome, idiopathic edema. y
Contraindication Adult renal insufficiency, significant renal impairment, anuria, hyperkalemia. Use cautiously in patient with fluid and electrolyte imbalance, impaired kidney function, or hepatic disease.
Side Effects CNS: headache, drowsiness,, lethargy, confusion, ataxia. GI: diarrhea, gastric bleeding, ulceration, caramping, gastritis, vomiting. GU: Impotence, menstrual disturbance HEMA: Agranulocytosis METABOLISM: Hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, mild acidosis, dehydration SKIN: uticaria, hirsutism, maculopapular eruptions, edematous rash.
Nursing responsibility 1. Monitor electrolyte levels, fluid I&O, weight, and BP. Give drug with meals to enhance absorption. Warn patient not to eat large amounts of potassium rich foods and not tonuse potassium containing salt substitute or use potassium supplements to prevent serious hyperkalemia. Give drug in the morning to avoid nocturia. Protect drug from light. Inform laboratory that patient is taking spironolactone because it may interfere with some laboratory tests that measure digoxin level.
2.
3.
4.
5. 6.
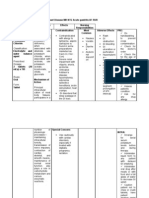
Drug Name Propanolol Hydrochloride 10mg BID y
Action Beta-blocker; antihypertensive , anti-anginal, antiarrhythmic Reduces cardiac O2 demand by blocking catecholamineinduced increases in heart rate, blood pressure, and force of myocardial contraction. Depresses rennin secretion and prevents vasodilation of cerebral arteries. y
Indication Angina pectoris, mortality reduction after M.I.; supraventricular, ventricular and atrial arrhythmias; tachyarhythmias caused by excessive catecholamine action during anesthesia. HPN Prevention of frequent, severe uncontrollable, or disabling migraine or vascular headache. Essential tremor. Hypertrophic subaortic stenosis. y
Contraindication Patient with bronchial asthma; sinus bradycardia, heart block greater than 1st degree, cardiogenic shock, overt cardiac failure. Use continuously in patients taking other hypertensive and in those with renal impairment, non allergic bronchospastic disease.
Side Effects CNS:fatigue; lethargy, vivid dreams, fever, hallucinations, menal depression, dizziness. CV: bradycardia, hypotension, heart failure, intermittent cloudication. GI: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,constipation. Hematologic: Agranulocytosis. Musculoskeletal: Orthralgia. Respi: Increased airway resistance. Skin: Rash.
Nursing responsibility 1. Check patients apical pulse before therapy. If extreme decrease in pulse rate occur, don t give the drug and immediately call the prescriber. Give oral drug with meals. Food may increase absorption. Double check dose and route. IV doses are much smaller than oral doses.
2.
y y
3.
y y
Drug Name Ceftriaxone Sodium
Action 3rd generation cephalosporin; antibiotic. Inhibits cell wall synthesis promoting osmotic instability, usually bactericidal.
Indication Treatment of susceptible infection; chancroid, endocarditis and surgical infection and gonorrhoea.
Contraindication History of shock; hypersensitivity to cephalosporins, penicillins, onilide local anesthesia.
Side Effects CNS: headache, dizziness, fever GI: pseudomembranoous colitis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dysguesia. CU: genital pruritus and candidiasis. Hematologic: Eosinophilia, thromocytosis, leukopenia. Skin: Phlebitis, rash.
Nursing responsibility 1. Ask patient about previous reaction to cephalosporins or penicillin before giving the dose. Be alert for adverse reaction; if adverse GI reactions occurs, monitor patient s hydration. Instruct patient to report pain at the IV site.
2.
3.
Drug Name Tramadol Hydrochloride 50mg q80
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects CNS: dizziness, vertigo, headache, somnolence, CNS stimulation, asthenia, anxiety, confusion, coordination disturbance, malaise, euphoria, nervousness, sleep disorder, seizures. CV: vasodilation EENT: visual disturbance GI: nausea, constipation, vomiting, dyspepsia, dry mouth, diarrhea, abdominal pain, anorexia, flatulence GU: urine distention, urinary frequency, menopausal syndrome Skin: pruritus, sweating, rash 1. 2.
Nursing responsibility Monitor CV and respiratory status. If respiratory rate decreases or falls below 12bpm, withhold dose and notify prescriber. Assess patients pain before starting therapy and regularly thereafter to monitor the drug s effectiveness. Closely monitor patient risk for seizure; drug has been reported to reduce seizure threshold. Monitor patient for drug dependence; tramadol can produce dependence similar to that of codein or dextropropoxyphene and thus has potential to be abused. For better effect, give drug before onset of intense pain. Because constipation is a common adverse effect, anticipate need for laxative.
y y
Opioid against analgesic Centrtally acting synthetic analgesic compound not chemically r/t opioid that is thought to bind to opioid receptors and inhibit reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin. Relieves pain.
Moderate to severe pain.
Contraindicated to patients hypersensitive to the drug or any of its components and in those and acute intoxication from alcohol, hypnotics, centrally acting analgesics, opioids, or psychotrophic drugs. Use cautiously in patients risk for seizures or respiratory depression, patient with increase ICP or head injury, acute abdominal conditions, or renal hepatic impairment, and patients physically dependent to opioids.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Drug Name Phytonadione (Vit. K) 1amp q8o y
Action Synthetic analysis of vitamin K. Blood coagulation modifier. An antihemorrhagic factor that promotes hepatic formation of active prothrombin. Controls abnormal bleeding. y
Indication Hyperprothromb in secondary to vitamin K malabsorption, drug therapy, or excessive vitamin A. Hypoprothrombi nemia secondary to effect of oral anti coagulants. Prevents hemorrhagic disease in newborns. y
Contraindication Contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components.
Side Effects CNS: dizziness, seizure like movements CV: flushing, trancient hypotension after IV administration, rapid and weak pulse, cardiac irregularities. Skin: diaphoresis, erythema
Nursing responsibility 1. Monitor patient to determine dosage effectiveness. Check brand name labels for administration route restrictions. SC is the preferred route for administration.
2.
3.
Drug Name Metronidazole 500mg IV q6o y
Action Antibacterial, antiprorozoal, amebecide. Direct acting trichomonacide and amebicide that works at both intestinal and extraintestinal site. Hinders growth of selected organiz=sms including most aerobic bacteria and protozoa. y
Indication Amebic hepatic abscess; intestinal y
Contraindication Contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to the drug or other nitroimidazole derivatives. Use cautiously in patient receiving hepatotoxic drugs and in patient with history of blood dyscrasia or CVS disorder. y
Side Effects Nausea, headache, anorexia, occasionally vomiting, diarrhea, epigastric cramping, constipation, leukopenia.
Nursing responsibility 1. Watch carefully for edema, especially in patient also receiving corticosteroids, because flagyl IV PTU may cause Na retention. Tell patient that metallic taste and dark or red urine may occur. Give with meals to minimize GI distress. Flagyl ER at least 1o before or 2o after meals.
2.
3.
Drug Name Kalium Durule 1durule TID y y
Action Hypokalemia Prophylaxis during treatment of diuretics Prevent and treat potassium deficit secondary to diuretics y
Indication Supplemental potassium in the form of high KCL may be able to restore normal potassium levels. y
Contraindication Renal insufficiency, hyperkalemia, unrelated addisons, constriction of the esophagus and/or destructive changes in the alimentary tract. y y y y y
Side Effects Hyperkalemia Nausea and vomiting Irritability Muscle weakness Dysphagia
Nursing responsibility 1. 2. Monitor BP and PR. This medicine must be completey dissolved in at least glass of cold water to reduce its possible stomach irritating/ laxative effects. Don t use salt substance, eat low salt diet. Monitor color of stools blackish stoolsmay indicate stomach/intestin al bleeding.
3.
4.
You might also like
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Drug Study 68-75Document8 pagesDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyKenneth ManalangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- Icu Drug StudyDocument7 pagesIcu Drug StudyHazel Palomares100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyCris Constantino San JuanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Mefenamic Acid: CefuroximeDocument9 pagesMefenamic Acid: CefuroximeGregory LitangNo ratings yet
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocument12 pagesDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument22 pagesFinal Drug StudyPaula Xavier AlfalahiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument15 pagesDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ProjectDocument7 pagesDrug Study ProjectMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NewDocument4 pagesDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studyjanelee2824No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFritzie Beatrice NomusNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- ECLAMPSIA Drug StudyDocument10 pagesECLAMPSIA Drug Studyjessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyEzshkha OngueNo ratings yet
- VIII. Drug StudyDocument11 pagesVIII. Drug StudyCharlayne AnneNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyCrystal Joy MisaNo ratings yet
- Drug StuyJJASGHDocument7 pagesDrug StuyJJASGHJan Pierre RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyNajmah Saaban100% (1)
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Medications ConferenceDocument68 pagesCovid 19 Medications ConferenceSaraNo ratings yet
- CHH Drug Study Week 3Document21 pagesCHH Drug Study Week 3maryxtine24No ratings yet
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pages5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument17 pagesDrugsRenzkie GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument6 pagesDrug Name Classification and Mechanism of Action Indication/ Dosage/ Route Contraindicatio N Adverse Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Drug Study Medcor AguinaldoDocument6 pagesDrug Study Medcor AguinaldoYana PotNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Hemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Document4 pagesHemostan, Methergine CA Gluconate2Stacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyRye IbarraNo ratings yet
- CHH Drug Study Week 2Document25 pagesCHH Drug Study Week 2maryxtine24No ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Substances AbuseDocument4 pagesDrugs For Substances AbuseAriadne MangondatoNo ratings yet
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyFloramae Celine BosqueNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument5 pagesDrugsJicel Camille EdeaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ICUDocument4 pagesDrug Study ICUArthadian De PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventDocument6 pagesAmlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)