Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04 - Power Supply
Uploaded by
Amit Kumar MudgalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
04 - Power Supply
Uploaded by
Amit Kumar MudgalCopyright:
Available Formats
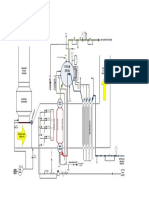
By: Satya Pal, A.D.E.
The Input Filter Circuit suppresses,
simultaneously with suppression of external noise, the noise produced by the switching circuits to prevent the noise form being transmitted to external circuits.
The Rectifier Circuit, used for rectifying the AC
voltage to the DC voltage, is of a capacitor input type which has a chock coil inserted for improving the power factor.
The rush-current preventive circuit
suppresses the such current by means of a resistor inserted into the input line, and reduces the loss of the resistor by actuating a thyristor after the D/D converter is started.
The D/D converter converts the DC voltage
into 50 V DC output. This converter has been designed in doubleforward type using power MOSFETs in consideration to small size and efficiency. The working frequency of the converter is about 400 MHz.
This power circuit supplies power to the
protective and control circuits.
This protective circuit detects continuously
the primary input voltage and the input rectified voltage of the D/D converter, and interrupts the power supply to the converter, turning the output of the converter OFF, if the primary input voltage is abnormally low. Furthermore, if in the normal primary voltage one of three wires (for three phases) becomes open, the protective circuit turns the output of this Power Supply OFF.
The control circuit controls ON/OFF operation
of the D/D converter at the time of undercurrent input, overvoltage output or actuation of the overheat protective circuit, or by external PS CONT signal.
This protective circuit detects continuously
each secondary output voltage. If the output voltage rises abnormally, the protective circuit makes notching, thus turning the output OFF.
This protective circuit detects continuously
the primary switching current of each D/D module, and makes notching if the output current exceeds the rating owing to such a reason as overload, thus turning the output OFF.
This protective circuit detects continuously
each output voltage. When the output voltage rises normally, the protective circuit sends out a PS ON ANS signal.
If the overvoltage, overcurrent or
undervoltage protective circuit is actuated, the notching alarm circuit interrupts the operation of the D/D converter for about 4 sec and at the same time when the converter output is stopped, this circuit makes the ALM (LED) on the front panel light and sends out a PS FAULT signal. The notching count time is about 30 sec, and when the notching is counted four times in the period of 30 sec, the notching alarm circuit actuates the NFB, interrupting the primary input voltage.
If the notching is not counted four times in
this period of 30 sec, the notching count is reset, and the alarm circuit automatically returns to normal condition of regular operation.
If the internal temperature of the Power
Supply rise abnormally for such a reason as discontinuation of the cooling, the overheat protective circuit actuates the NFB, thus interrupting the primary input voltage.
This metering circuit detects each output
voltage and send out the voltage for the metering.
In order for this power supply to be used with the best condition, check the following: Check that the input voltage, output voltage and output current are kept in the specified level. Check that external forced air cooling is operational. Check that binding screws of terminals and parts are not loosened. Make cleaning, if the power supply is dirty due to long term use.
The switching circuit is composed of two pairs
of MOSFETs and two transformers. Each pair of MOSFETs turn on automatically, and the voltage shown in the figure as below are applied to the transformers.
You might also like
- QP 201012 IIFT PaperDocument42 pagesQP 201012 IIFT PaperAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- IIFT 2008 PaperDocument51 pagesIIFT 2008 PaperAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- NCRT PageDocument1 pageNCRT PagedjangoroflNo ratings yet
- Work & EnergyDocument14 pagesWork & EnergyrjkmehtaNo ratings yet
- Iesc 1 AnDocument3 pagesIesc 1 AnrajeshbantaNo ratings yet
- Sci9 - 15 - Improvement in Food Reources PDFDocument13 pagesSci9 - 15 - Improvement in Food Reources PDFSwapna PriyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document14 pagesChapter 14anil.gelra5140No ratings yet
- Chap 12 Science IX NCERTDocument16 pagesChap 12 Science IX NCERTAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Fall IllDocument13 pagesWhy Do We Fall IllMothi KarunaNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 Science IX NCERTDocument15 pagesChap 10 Science IX NCERTAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Master the art of listening to build meaningful connectionsDocument13 pagesMaster the art of listening to build meaningful connectionsAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Naoparticles Based SensorsDocument7 pagesNaoparticles Based SensorsAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Materials & Magnetization MechanismsDocument103 pagesMagnetic Materials & Magnetization MechanismsAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Varactor TheoryDocument36 pagesVaractor TheoryAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Nano MedicinesDocument17 pagesNano MedicinesAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Technical Details DDDocument6 pagesTechnical Details DDAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Varactor TheoryDocument36 pagesVaractor TheoryAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Varactor TheoryDocument36 pagesVaractor TheoryAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Nanodevice I: Solid state and molecular electronicsDocument39 pagesNanodevice I: Solid state and molecular electronicsAmit Kumar MudgalNo ratings yet
- Mri Physics AacDocument196 pagesMri Physics AacAmit Kumar Mudgal100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- A Full Wave RectifierDocument14 pagesA Full Wave RectifierVarun Jain50% (6)
- Ee - Elective 1: Power System Protection 1Document22 pagesEe - Elective 1: Power System Protection 1Alyssa RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.1.1 The Principle of WindmillDocument22 pagesChapter-1: 1.1.1 The Principle of WindmillVijay BavikattiNo ratings yet
- Inverter Battery Sizing FaqDocument3 pagesInverter Battery Sizing FaqFull DocumentaryNo ratings yet
- KECBrochureDocument20 pagesKECBrochurePriyanka PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- GA EM2 Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesGA EM2 Lesson PlanAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- Energy TestDocument9 pagesEnergy Testa.largeNo ratings yet
- Steam boiler vent diagramDocument1 pageSteam boiler vent diagramSan DiNo ratings yet
- X Physics Segment 2 Q-BankDocument7 pagesX Physics Segment 2 Q-Bankavp sNo ratings yet
- 02-Sedecal Instalacion HF IN1005R5iDocument91 pages02-Sedecal Instalacion HF IN1005R5ijaime munozNo ratings yet
- 710-18929-00E L-Series MVE Brochure Global EN - WebDocument11 pages710-18929-00E L-Series MVE Brochure Global EN - WebThanh Tung NguyenNo ratings yet
- CT 200 DatasheetDocument2 pagesCT 200 Datasheetjeffv65No ratings yet
- I/O List for Sequence of Events RecorderDocument35 pagesI/O List for Sequence of Events Recordersrigirisetty208No ratings yet
- Generator Protection Relay VAMP 210iDocument3 pagesGenerator Protection Relay VAMP 210iYandri PaulusNo ratings yet
- SYNC CHECK BlankDocument6 pagesSYNC CHECK BlankimranNo ratings yet
- PSD Course File 2011-12Document40 pagesPSD Course File 2011-12Sethupathi CmNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Boiler Efficiency PDFDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Boiler Efficiency PDFEsra MarthenNo ratings yet
- Islanding of 24-Bus IEEE Reliability Test SystemDocument16 pagesIslanding of 24-Bus IEEE Reliability Test SystemRahul_KittuNo ratings yet
- Bohol Island Power Supply PlanDocument59 pagesBohol Island Power Supply PlanCaesar Rey Chico100% (1)
- Electrical Workshop Report Steel Cutting Machine ProjectDocument2 pagesElectrical Workshop Report Steel Cutting Machine ProjectAhmad Yon KhoerulNo ratings yet
- FinCap Solar Power SolutionsDocument2 pagesFinCap Solar Power SolutionspkchandaliaNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of EV HEV PDFDocument17 pagesModeling and Simulation of EV HEV PDFshawn liNo ratings yet
- Uncompromising Protection and Control for MotorsDocument56 pagesUncompromising Protection and Control for Motorsvvlike767No ratings yet
- Report RX87DRN100L4 TF 131332185591905454Document1 pageReport RX87DRN100L4 TF 131332185591905454Hugo Mario Ariza PalacioNo ratings yet
- ECE 576 Power System Dynamics and Stability Lecture NotesDocument28 pagesECE 576 Power System Dynamics and Stability Lecture Notes7harma V1swaNo ratings yet
- 6.6kV SWGRDocument142 pages6.6kV SWGRFounHeadNo ratings yet
- Blowdown (Mechanical Engineer's Reference Book)Document3 pagesBlowdown (Mechanical Engineer's Reference Book)Devi PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Ring Main Unit Testing and Commissioning Method StatementDocument4 pagesRing Main Unit Testing and Commissioning Method StatementAleen Gamal Al-DinjiNo ratings yet
- Mid 20-25KW KTL3XDocument2 pagesMid 20-25KW KTL3XwaqasNo ratings yet
- High Voltage High-Breaking Capacity VV Fuse-LinksDocument9 pagesHigh Voltage High-Breaking Capacity VV Fuse-LinksMochamadIrlanMalikNo ratings yet