Professional Documents
Culture Documents
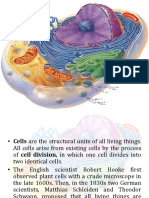
Cell organelles and their functions
Uploaded by
applegummyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell organelles and their functions
Uploaded by
applegummyCopyright:
Available Formats
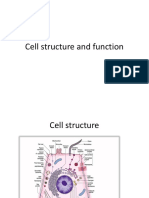
Nucleus Spherical in shape. Largest structure in the cell. Responsible for cell reproduction.
. Controls cell activities including repair of worn-out parts. Needed for cell to stay alive. Contains chromosome. Chromosome (a part of the nucleus) Long thread-like structures. Made up of proteins and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Presence of genes which contain hereditary materials. Passed down from their parents to their offspring. Cell membrane Thin membrane surrounding the cell.
Vacuole Fluid-filed spaces within the cytoplasm. Store water and other nutrients needed for the organism to survive. Small, numerous and temporary in animal cells. Lysosome Round organelles surrounded by a membrane. Contains digestive enzymes. Digestion of cell nutrients take place here. Nuclear membrane The membrane that surrounds the nucleus. Mitochondrion Spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. Inner membrane infolded many times forming cristae. Converts energy stored in glucose into adenosine triphosphate for the cell. Nucleolus An organelle within the nucleus. Where ribosomal RNA is produced. Ribosome Small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic granules that are sites of protein synthesis.
Partially permeable
Boundary between cell and external environment. Controls substances entering or leaving the cell. Cytoplasm Jelly-like substances. Contains chemicals and other tiny structures that carry out special functions. Golgi apparatus A flattened, layered, sac-like organelle Produces the membranes that surround the lysosomes.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum A vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted sacks that are in the cytoplasm. The ribosome covering it gives a rough appearance. Transport materials through the cell and produces proteins. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum A vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are in the cytoplasm.
Muscle tissue (Contractile tissue) Helps the body move by contracting. Collections of muscle cells. Complex tissue Contains several types of cells. Examples: Connective tissue, nervous tissue, glandular tissue. Connective tissue
Transports materials through the cell.
Contains enzymes and produces and digest lipids and membrane proteins. Smoother Endoplasmic Reticulum buds off from rough endoplasmic reticulum to move the newly-made proteins and lipids to the golgi body and membranes.
To connect different part of an organ or organs together.
Tissue found inside or between organs. Made up of a few types of cells. Nervous tissue Detecting changes and transmitting messages within the body. Epithelial tissue To protect the body from injuries. Sheets of cells which covers both internal and external surfaces. The sheets of cells covering the external surfaces is are called epidermis.
Made up of organs
Contains specialized cells and tissue. Tissue Same type of cells form a tissue. Examples: epithelial tissue (epithelium), muscle tissue (contractile tissue), epidermis (plant). Different tissues may be united to form an organ. Different tissues work together to perform a specific function.
Nucleus Spherical in shape.
Vacuole Fluid-filed spaces within the cytoplasm.
Largest structure in the cell.
Responsible for cell reproduction. Controls cell activities including repair of worn-out parts. Needed for cell to stay alive. Contains chromosome. Chromosome (a part of the nucleus) Long thread-like structures. Made up of proteins and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Presence of genes which contain hereditary materials. Passed down from their parents to their offspring. Cell membrane Thin membrane surrounding the cell. Partially permeable Boundary between cell and external environment. Controls substances entering or leaving the cell. Cytoplasm Jelly-like substances. Contains chemicals and other tiny structures that carry out special functions. Nuclear membrane The membrane that surrounds the nucleus.
Store water and other nutrients needed for the organism to survive.
Small, numerous and temporary in animal cells. Chloroplast Contains chlorophyll which is needed to absorb energy from the Sun to photosynthesis.
Cell wall
A thick layer surrounding the cell membrane. Made up of cellulose. Supports the cell. Gives the cell a regular shape. Golgi apparatus
A flattened, layered, sac-like organelle
Produces the membranes that surround the lysosomes. Mitochondrion Spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. Inner membrane infolded many times forming cristae. Converts energy stored in glucose into adenosine triphosphate for the cell. Nucleolus An organelle within the nucleus. Where ribosomal RNA is produced.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Epithelial tissue To protect the body from injuries. Sheets of cells which covers both internal and external surfaces. The sheets of cells covering the external surfaces is are called epidermis. Muscle tissue (Contractile tissue) Helps the body move by contracting. Collections of muscle cells. Complex tissue Contains several types of cells. Examples: Connective tissue, nervous tissue, glandular tissue. Connective tissue To connect different part of an organ or organs together. Tissue found inside or between organs. Made up of a few types of cells. Nervous tissue Detecting changes and transmitting messages within the body.
A vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted sacks that are in the cytoplasm.
The ribosome covering it gives a rough appearance. Transport materials through the cell and produces proteins. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum A vast system of interconnected, membranous, infolded and convoluted tubes that are in the cytoplasm. Transports materials through the cell. Contains enzymes and produces and digest lipids and membrane proteins. Smoother Endoplasmic Reticulum buds off from rough endoplasmic reticulum to move the newly-made proteins and lipids to the golgi body and membranes. Made up of organs Contains specialized cells and tissue. Tissue Same type of cells form a tissue. Examples: epithelial tissue (epithelium), muscle tissue (contractile tissue), epidermis (plant). Different tissues may be united to form an organ. Different tissues work together to perform a specific function.
You might also like
- Cells: By: Ms. ReisDocument24 pagesCells: By: Ms. ReisZohaib Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- 2 Cca IVD3 LX 0 F Zxy 7 NR 06914 J6 LG7 M 1 KM Oad ZNC IlDocument38 pages2 Cca IVD3 LX 0 F Zxy 7 NR 06914 J6 LG7 M 1 KM Oad ZNC IlLara AminNo ratings yet
- C2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismDocument39 pagesC2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismyourmoNo ratings yet
- Bly 111 Cell and Cell Structure-1Document32 pagesBly 111 Cell and Cell Structure-1stephenalfa7No ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: Siva PrasadDocument28 pagesCells and Tissues: Siva PrasadAWS DEVELOPERNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell: Vincent RodriguesDocument18 pagesEukaryotic Cell: Vincent RodriguesPeaches HagleyNo ratings yet
- Human Cell AnatomyDocument56 pagesHuman Cell Anatomysanthiyasandy100% (3)
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument30 pagesCell Structure FunctionAngelo GabrielNo ratings yet
- CellDocument23 pagesCellErdis MerepezaNo ratings yet
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellDocument18 pagesGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellRasan QadrNo ratings yet
- Lec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument57 pagesLec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesSatyam AryaNo ratings yet
- Cell Types & Cell ModificationDocument41 pagesCell Types & Cell ModificationShane Marcande Calicdan78% (18)
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument37 pagesCell Structure & FunctionAtika Ayu KusumaningtyasNo ratings yet
- The Cell 1Document66 pagesThe Cell 1Patricia JalbanNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic CellDocument24 pagesEukaryotic CellVassudev KamatNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument33 pagesCell Structure and FunctionNaveelaNo ratings yet
- Cell & Its OrganelleDocument66 pagesCell & Its OrganellerookieNo ratings yet
- 5-Cell StructureDocument65 pages5-Cell StructureShydene SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell - Structure - FunctionDocument94 pagesLecture 3 Cell - Structure - FunctionMuhammad Abbas WaliNo ratings yet
- CellDocument34 pagesCellSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- Cell structure and key organellesDocument22 pagesCell structure and key organellesISRAELNo ratings yet
- Reviewing General Biology IDocument9 pagesReviewing General Biology IRuby May Regala100% (9)
- The Cell: A Generalized Cell and Its Main OrganellesDocument22 pagesThe Cell: A Generalized Cell and Its Main OrganellesSeira SusaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: A Guide to the OrganellesDocument11 pagesCell Structure: A Guide to the OrganellesAli MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic CellDocument19 pagesEukaryotic CellSameer MohammedNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument43 pagesCell StructureKexinNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument2 pagesThe Cellrosana f.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument28 pagesAnimal CellSahir koleNo ratings yet
- Cell Components: See This VideoDocument28 pagesCell Components: See This VideoDwika Puspa Wardhani 'Vreundschap'No ratings yet
- Cell and TransportDocument77 pagesCell and TransportEugenie Francisco100% (1)
- Cell Structure & Function 2022Document43 pagesCell Structure & Function 2022Kavita MahaseNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Its Function DLLDocument62 pagesCell Parts and Its Function DLLRovelyn AlejoNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Cell StructureDocument3 pages2.1. Cell StructureAyesha AzizNo ratings yet
- General Physiology by BrownDocument51 pagesGeneral Physiology by BrownuzohchukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument55 pagesWeek 2 - Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellsz4g4v7gkzjNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologyDocument41 pagesFundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologySmitha JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- Lesson3-TheCellDocument27 pagesLesson3-TheCelly041087No ratings yet
- Generalized animal cell organelles and functionsDocument13 pagesGeneralized animal cell organelles and functionsMa Ronalyn Abogne SigueNo ratings yet
- Introduction (2015 - 06 - 09 13 - 02 - 59 UTC)Document97 pagesIntroduction (2015 - 06 - 09 13 - 02 - 59 UTC)DiazNo ratings yet
- Combined Powerpoints On Cells 2017Document66 pagesCombined Powerpoints On Cells 2017api-242405009No ratings yet
- The cell: A basic unit of structure and functionDocument73 pagesThe cell: A basic unit of structure and functionketyleenbNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: A Guide to Structure and FunctionDocument137 pagesCells and Tissues: A Guide to Structure and FunctionSkarlon BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Biology Basic ConceptsDocument6 pagesBiology Basic ConceptsAhsni128No ratings yet
- As 1Document9 pagesAs 1Shagufta Jasmin SubiNo ratings yet
- The Cell Notes PDFDocument8 pagesThe Cell Notes PDFhi.blessNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument55 pages2 Cell Structure and FunctionRiz MarieNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument76 pagesCell Structure & Functionuday xeroxNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument38 pagesCellsMaryam SabirNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and Skeleton. Ms Mutembedza: The CellDocument24 pagesCells, Tissues and Skeleton. Ms Mutembedza: The Celltadiwanashe alvinNo ratings yet
- The Cell Organelles Group 2Document4 pagesThe Cell Organelles Group 2gayetamapaulinemaeNo ratings yet
- Structure of Cell Libra LDHDocument28 pagesStructure of Cell Libra LDHapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Cell Biology BasicsDocument6 pagesCell Biology BasicsEllyn De chavezNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesLESSON 3 Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsSophia CamachoNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: J.C.CatolicoDocument85 pagesCells and Tissues: J.C.CatolicoGynew0% (1)
- Cell StructureDocument53 pagesCell Structuremuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument53 pagesCell Structuremuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organelles: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument39 pagesCells and Organelles: The Building Blocks of LifekdjskfsNo ratings yet
- The Basic Structural and Functional Unit of Life - The CellDocument87 pagesThe Basic Structural and Functional Unit of Life - The CellLovely Ann LoyogoyNo ratings yet
- General Science Reviewer For LET 2022Document117 pagesGeneral Science Reviewer For LET 2022Elaine May Cabunoc GalvezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Medical Terminology Verified AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Medical Terminology Verified AnswersGregg ProducerNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Budget of WorkDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Budget of WorkMaricris BalboaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of the Fully Automated Urinalysis Analyzers UX-2000 and Cobas 6500Document10 pagesComparison of the Fully Automated Urinalysis Analyzers UX-2000 and Cobas 6500Sethulakshmi PharmacistNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Building DNADocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Building DNAMia Smith100% (1)
- Bioinformatic Analysis of HBBDocument1 pageBioinformatic Analysis of HBBfrank2689No ratings yet
- E-Portfolio Injection Study GuideDocument7 pagesE-Portfolio Injection Study Guideapi-366034042No ratings yet
- Trunking CatalogDocument8 pagesTrunking CatalogDenuka PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Life in The Deserts Worksheet 2Document2 pagesLife in The Deserts Worksheet 2Uma TiwariNo ratings yet
- 01 MDCAT SOS Regular Session (5th June-2023) With LR..Document5 pages01 MDCAT SOS Regular Session (5th June-2023) With LR..bakhtawarsrkNo ratings yet
- When The Koel SingsDocument15 pagesWhen The Koel SingsAlfie Paduga BeguinaNo ratings yet
- SOP EcoliDocument3 pagesSOP EcoliIeqa HaziqahNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) PropertiesDocument13 pagesCharacterization of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) PropertiesEsteban ArayaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Protista: Diverse Eukaryotic MicroorganismsDocument79 pagesKingdom Protista: Diverse Eukaryotic MicroorganismsMeah PachecoNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Operation - 030129Document8 pagesCooling Tower Operation - 030129Sekar CmNo ratings yet
- Amazing Facts - Exercises 1Document3 pagesAmazing Facts - Exercises 1Alina DorobatNo ratings yet
- Metals: Methods To Evaluate Corrosion in Buried Steel Structures: A ReviewDocument21 pagesMetals: Methods To Evaluate Corrosion in Buried Steel Structures: A ReviewPeymanMajidiNo ratings yet
- 4546-LacOperon InstsDocument14 pages4546-LacOperon InstsScribd_is_GreatNo ratings yet
- Mejasco, Bianca Isabelle A. - Block H - SGD #1Document2 pagesMejasco, Bianca Isabelle A. - Block H - SGD #1Bianca MejascoNo ratings yet
- Introspect For DealersDocument13 pagesIntrospect For DealersOBERON-INTROSPECT-BIOSPECTNo ratings yet
- Van Nostrands Scientific EncyclopediaDocument3,529 pagesVan Nostrands Scientific EncyclopediaMarius Popa100% (28)
- Gene TherapyDocument1 pageGene TherapyJenevieve B. CañeteNo ratings yet
- Dna Finger PrintingDocument23 pagesDna Finger PrintingSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Thephysiologyofincarnationprocess PDFDocument14 pagesThephysiologyofincarnationprocess PDFGabriel OzórioNo ratings yet
- Young Children's Biological Predisposition To Learn in Privileged DomainDocument6 pagesYoung Children's Biological Predisposition To Learn in Privileged DomainVeronica Dadal0% (1)
- Natamycin Story - What You Need to KnowDocument13 pagesNatamycin Story - What You Need to KnowCharles MardiniNo ratings yet
- Turbidimetry and Nephelometry1Document3 pagesTurbidimetry and Nephelometry1maxim_crank6101100% (1)
- Effects of Different Fermentation Temperatures On Metabolites of KimchiDocument7 pagesEffects of Different Fermentation Temperatures On Metabolites of KimchiAngela ValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- Science Holidays Homework Class 9Document2 pagesScience Holidays Homework Class 9nileshNo ratings yet
- Mengenali Konflik Dalam Negosiasi Oleh: Zumaeroh: PendahuluanDocument47 pagesMengenali Konflik Dalam Negosiasi Oleh: Zumaeroh: PendahuluanrahmatNo ratings yet
- Self Concept Inventory Hand OutDocument2 pagesSelf Concept Inventory Hand OutHarold LowryNo ratings yet